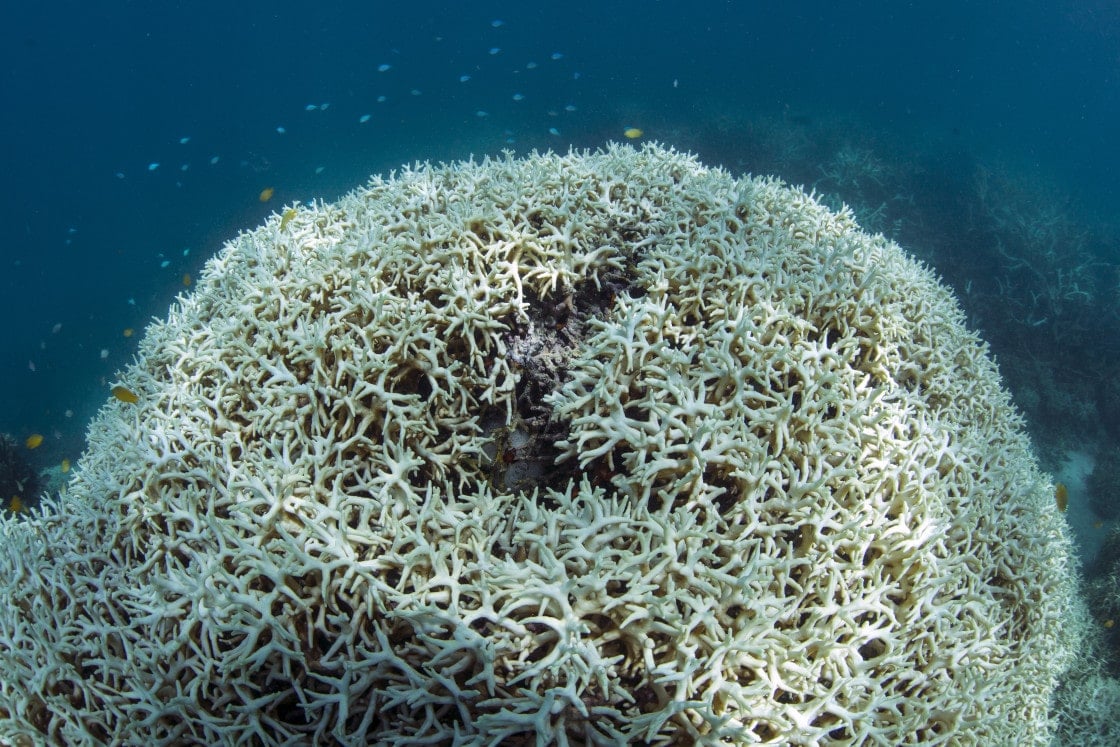

The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species is warning that over 44% of reef-building coral species globally are at risk of extinction.
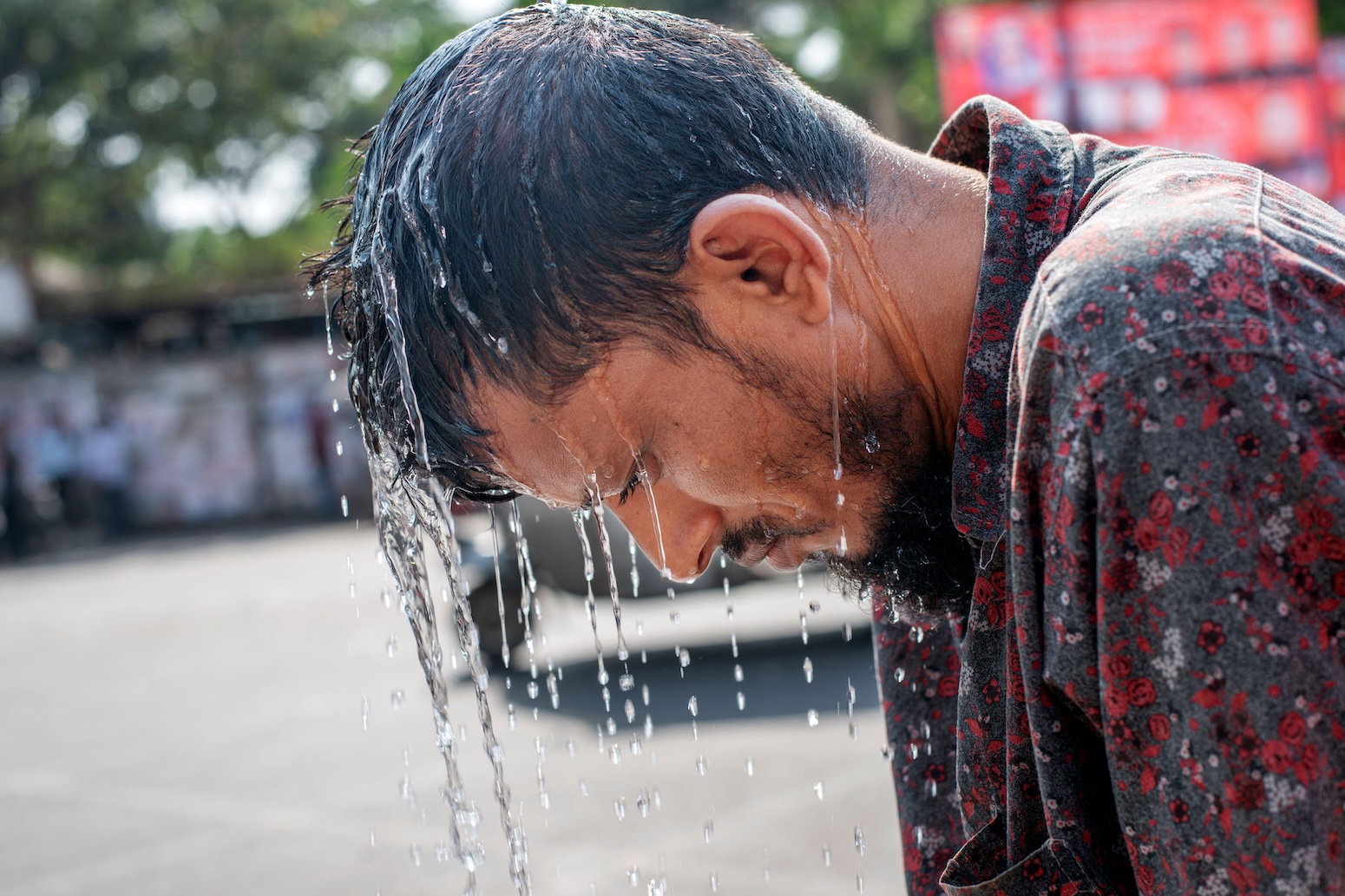

This year is now virtually certain to beat 2023 as the hottest year on record. It will also be the first full year to surpass 1.5C above pre-industrial levels across the majority of observational records.

The carbon footprint from private jet travel grew 46 % between 2019 and 2023 and will keep rising unless the ultra-luxury industry is regulated, according to a new research.

Greenhouse gas levels surged to a new record in 2023, committing the planet to rising temperatures for many years to come. CO2 is accumulating in the atmosphere faster than any time experienced during human existence.

A recent study has found that seafood mislabelling is running rampant in Calgary, and that certain product names are more likely to hide species of conservation concern.

Knowing how high-potency cannabis alters gene activity may bring us closer to understanding why some users develop psychosis.

In a study from 2022, researchers issued a "warning to humanity" about the consequences of tree losses, backed by 45 other scientists from 20 different countries.
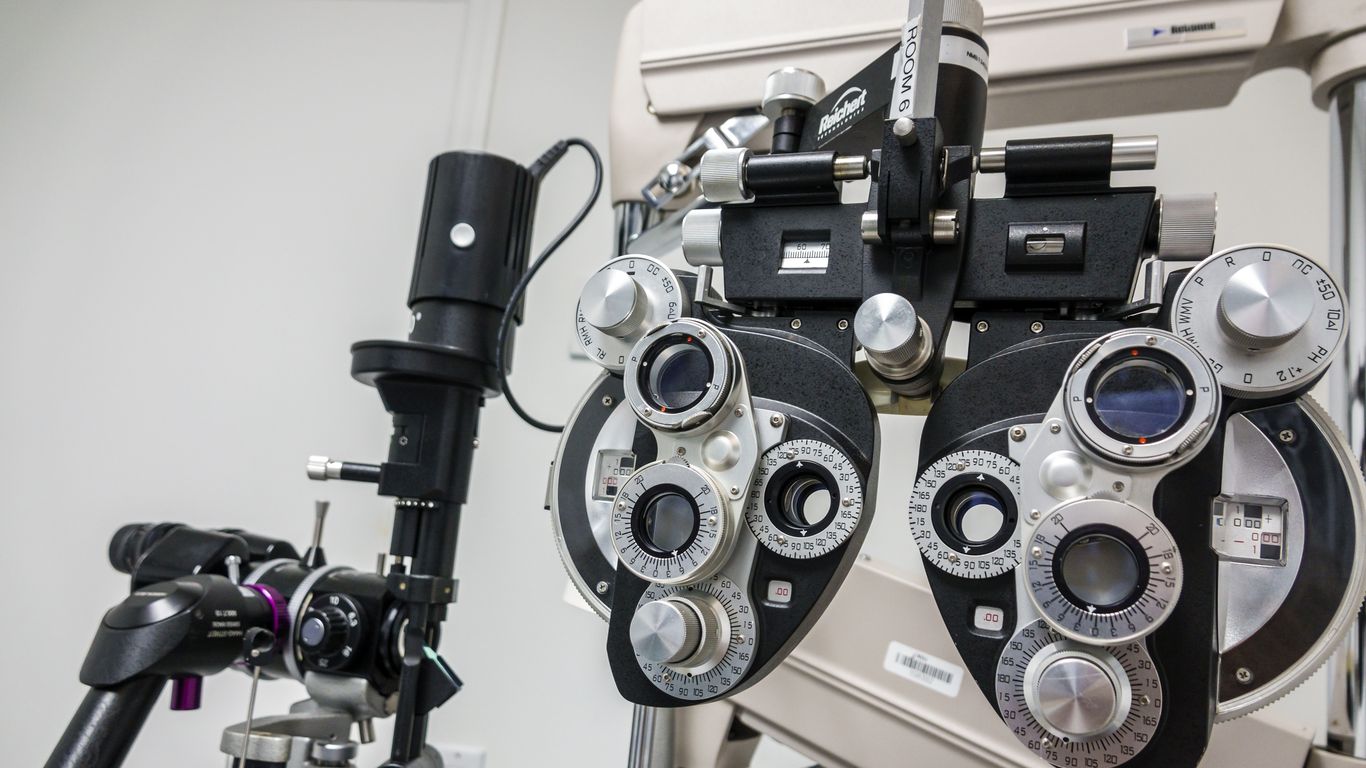
Approximately one-third of children and teens worldwide are nearsighted — a figure that's more than three times higher than it was in 1990, according to a UK study.

Our planet will only remain able to provide even the most basic standard of living for everyone in the future if economic systems and technologies are dramatically transformed and critical resources are more fairly used, managed and shared.

Methane concentrations in Earth's atmosphere increased at record speed over the past five years. At least two-thirds of annual methane emissions now come from human activities.

A study of more than 700 counties across multiple U.S. states found a link between childhood leukemia and levels of decaying radon gas, including those lower than the federal guideline for mitigation.
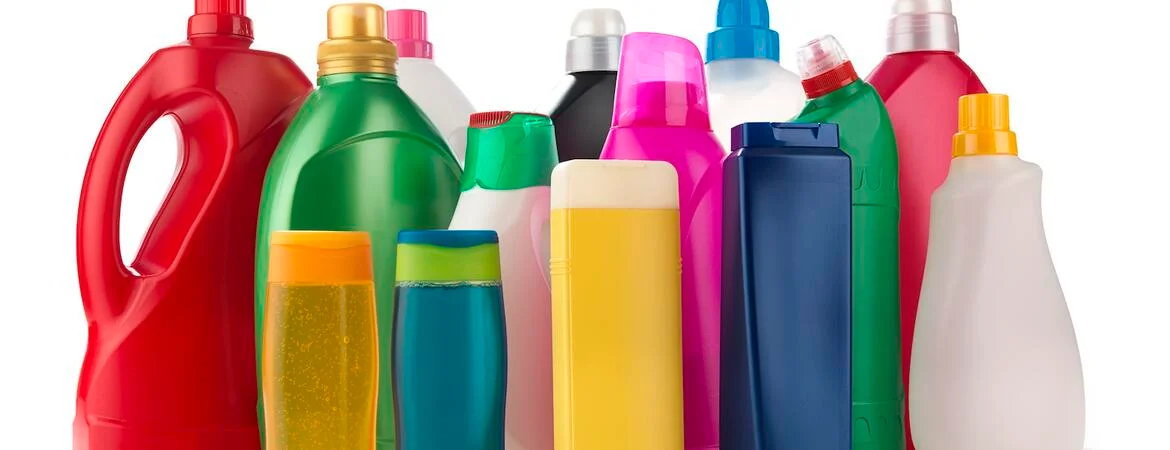

A new study documents how Southern Californians in U.S. are chronically being exposed to toxic airborne chemicals called plasticizers, including one that's been banned from children's items and beauty products.

Even with rapid emission cuts, some level of continued acidification may be unavoidable due to the CO2 already emitted and the time it takes for the ocean system to respond.
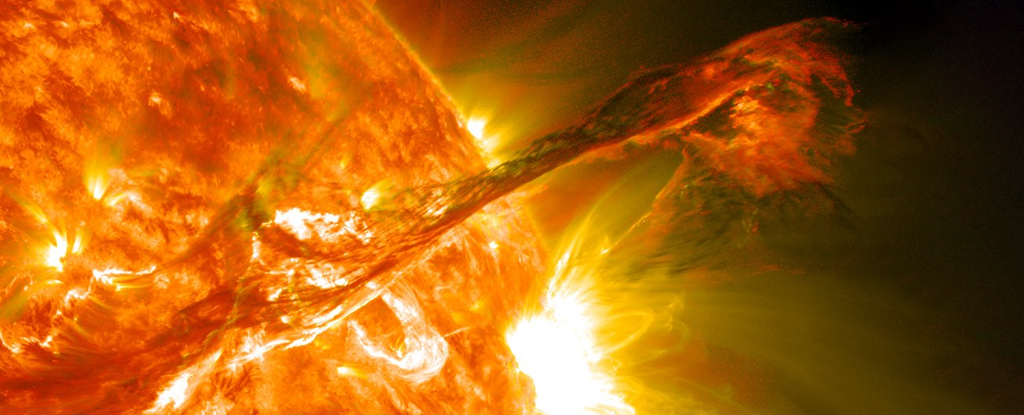

Extreme solar storms could spell disaster for our highly technological society because they have the potential to damage satellites and bring down communications networks and global electricity grids.

The sea surface temperature in the Fijian archipelago in the southwestern Pacific is now at its maximum for more than 600 years.