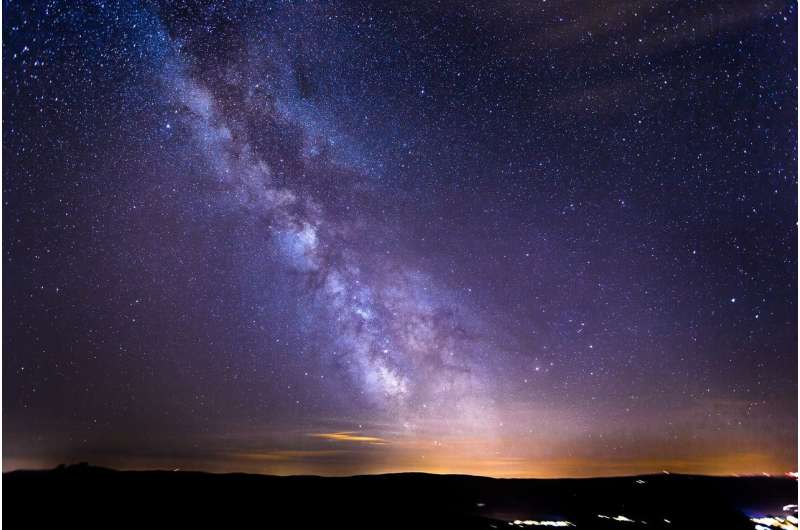

New research has uncovered a striking link between the structure of our galaxy and the evolution of Earth's crust, showing its development was shaped by the impact of meteorites during its journey through the Milky Way.
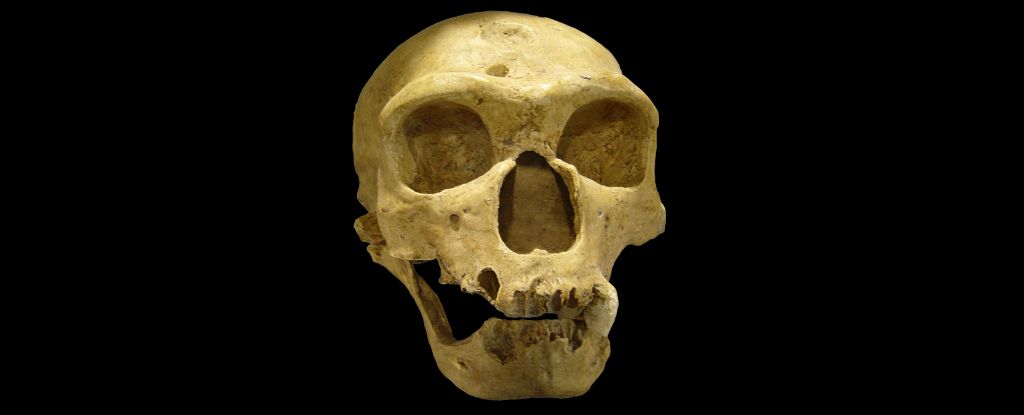
A new research suggests that a shift in the Earth's magnetic poles around 41,000 years ago, known as the Laschamp event, may have contributed to the extinction of Neanderthals.
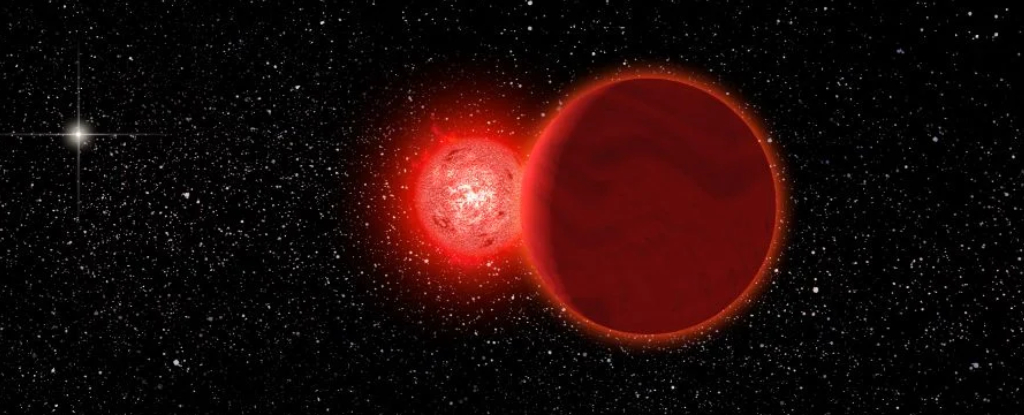

About 70,000 years ago Scholz's star passed through the Oort Cloud. It may have perturbed some comets from the Oort Cloud. But we won't know for a couple of million years because that's how long it would take for a comet to reach us.

New research uncovers the strongest solar event ever detected - rewriting our understanding of space weather and radiocarbon dating.

On 14 May 2025, the Sun erupted with the biggest flare we've seen all year.

At least two mass extinction events in Earth's history were likely caused by the "devastating" effects of nearby supernova explosions, a new study suggests.

Millions of years ago, our Solar System traveled through a densely populated galactic region and was exposed to increased interstellar dust.
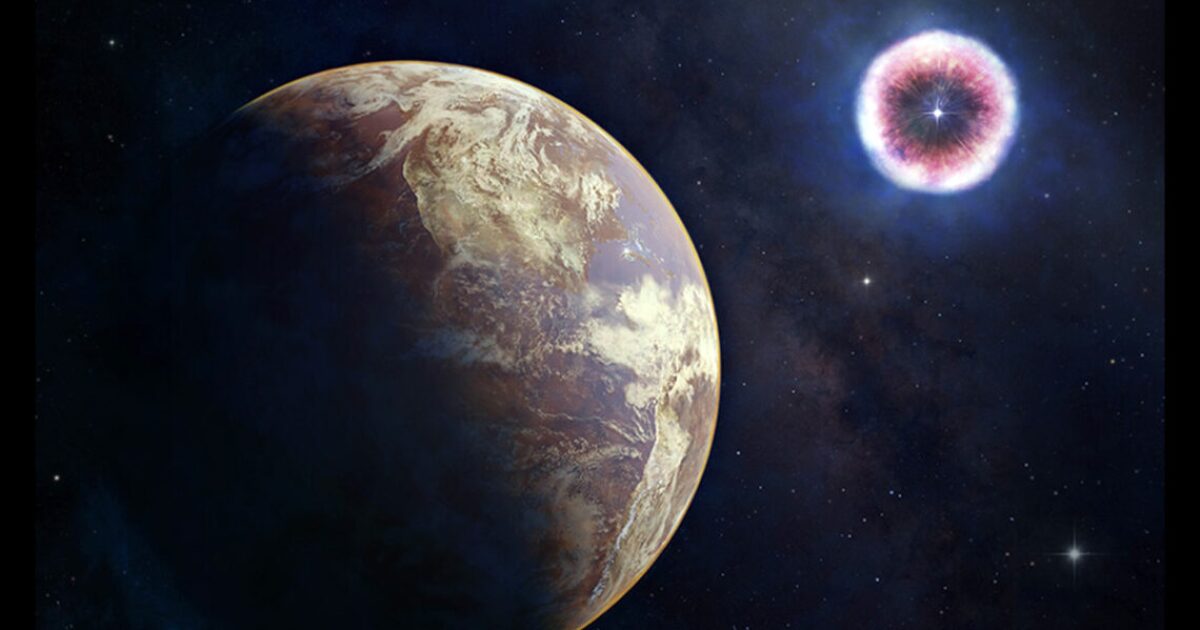

Scientists have traced radioactive elements on the seafloor back to the cosmic explosions they might have come from – and potentially linked the event to evolutionary changes in viruses in a lake in Africa.
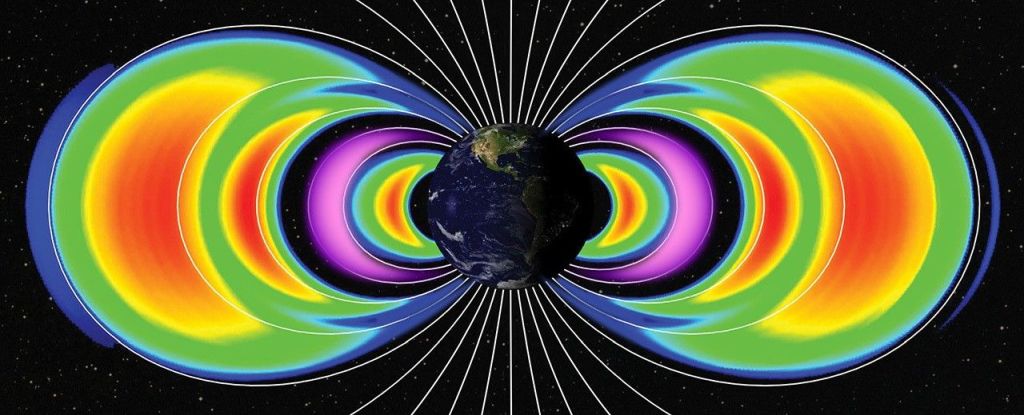

In the months following massive solar storm in May, 2024, Earth was girded by two new, temporary radiation belts of high-energy particles, trapped by the planet's magnetic field.
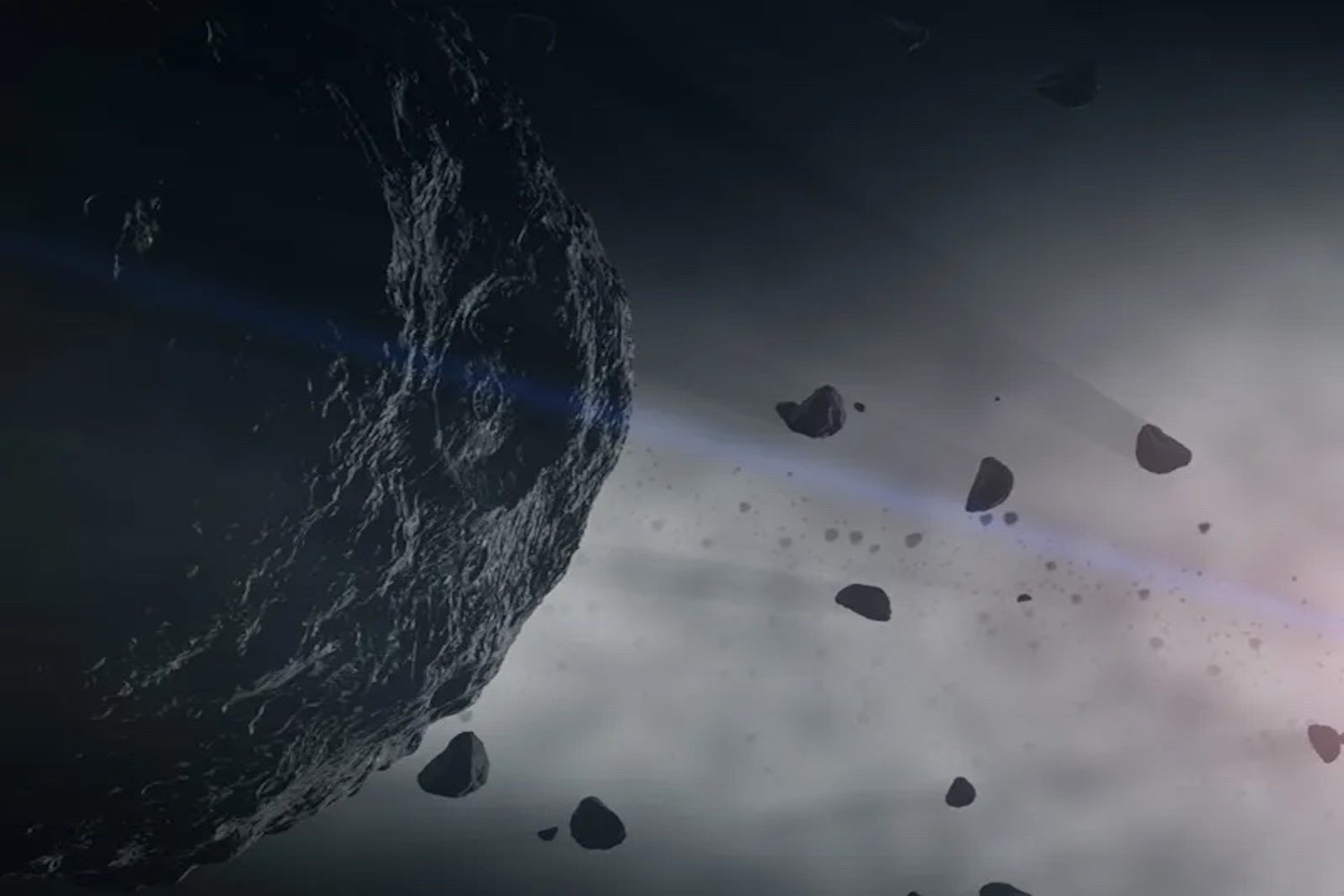

Bennu has a 1-in-2,700 chance of colliding with Earth in 2182, causing a global winter and drought.

Scientist have concluded water did not arrive as early during Earth's formation as previously thought.
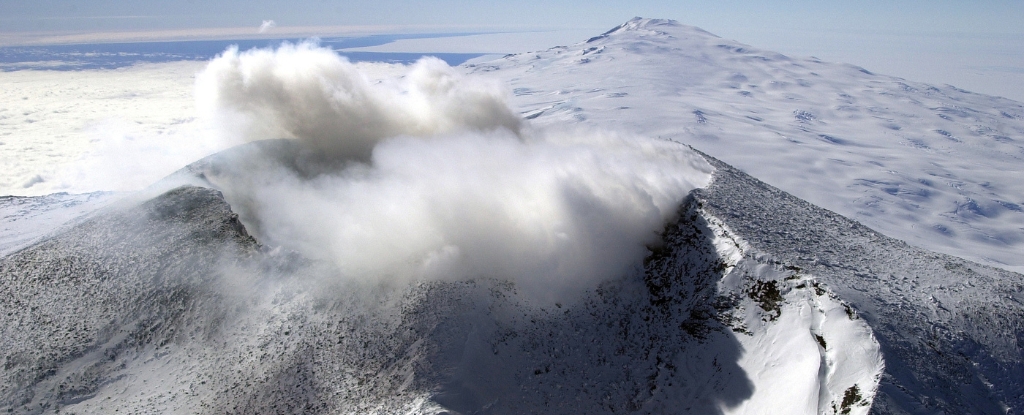

Deep under the frozen desert of western Antarctica, a hidden danger slumbers. Lurking beneath the massive, 1–2 kilometer-thick slab of frozen water lies an active volcanic rift, seething away in the deep, in the darkness.

If Earth is going to be blown to bits by an asteroid, it'd be nice to have some advance warning and a newly developed equation gives us a better chance of an early heads up.
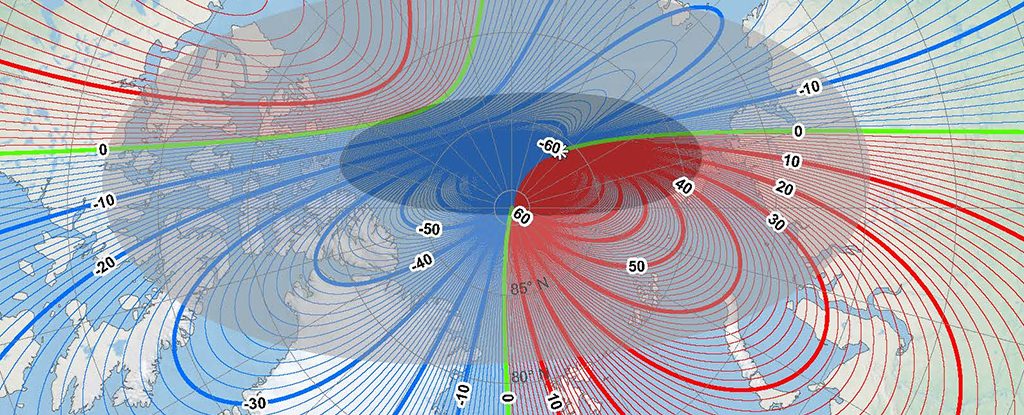
It's time to recalibrate the navigation systems on ships, airplanes: the position of the magnetic North Pole is officially being changed, continuing its shift away from Canada and towards Siberia.

A new analysis of the eruption rates of 56,400 Sun-like stars has estimated that the Sun's superflare rate is at the low end of that scale – once every 100 years.