
There’s growing optimism that huge amounts of natural hydrogen are stored deep underground. Now, researchers have identified the key geological features that could help us hunt for the clean-burning fuel.

Japan tests the most powerful solar panel in history, equivalent to 20 nuclear power plants; benefits and global implications of this groundbreaking technology.

Mankind has set out to use the Moon in aid of the first dark solar panel’s creation. This new type of photovoltaics is pioneering and will change how we power the Earth forever.

The air at sea might be getting a bit cleaner as technology group Wartsila puts its Carbon Capture Solution (CCS) system on the market. It is claimed to capture as much as 70% of the CO2 emissions from cargo ship exhaust systems.

Spruce trees anticipated a solar eclipse by syncing their signals. Older trees responded first. Forests may behave as one living system.

Scientists in Japan have developed a new type of plastic that's just as stable in everyday use but dissolves quickly in saltwater, leaving behind safe compounds.

With much of the developed world hastening its transition to renewables, take a look at some renewable megaprojects around the globe.
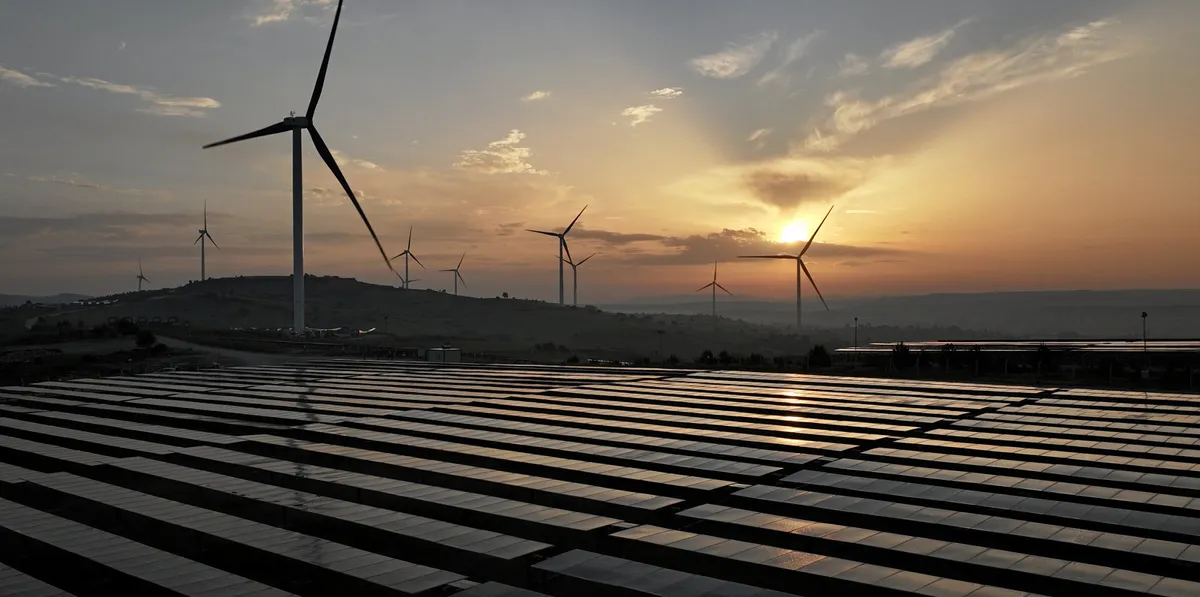

The world’s largest planned renewable energy project would be bigger than entire countries, with onshore wind turbines potentially triple the size of current market leading machines, according to new documents.

Switzerland is leading the way in clean energy with a world-first project: the installation of removable solar panels on active railway tracks.
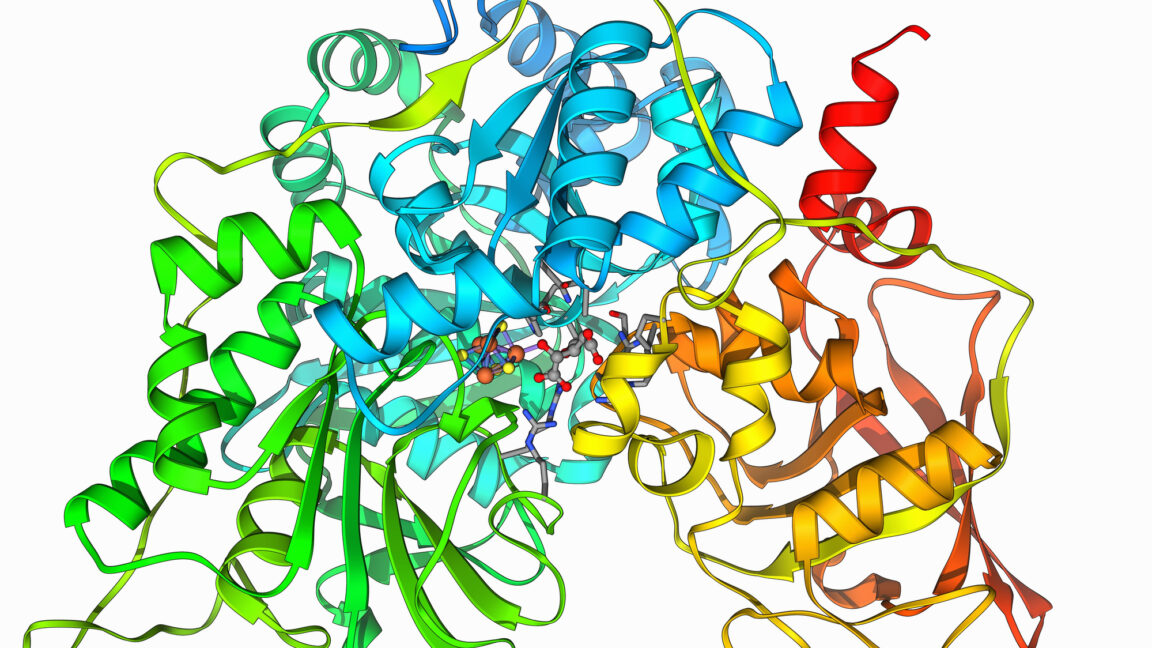
A new paper describes a success in making a brand-new enzyme with the potential to digest plastics.
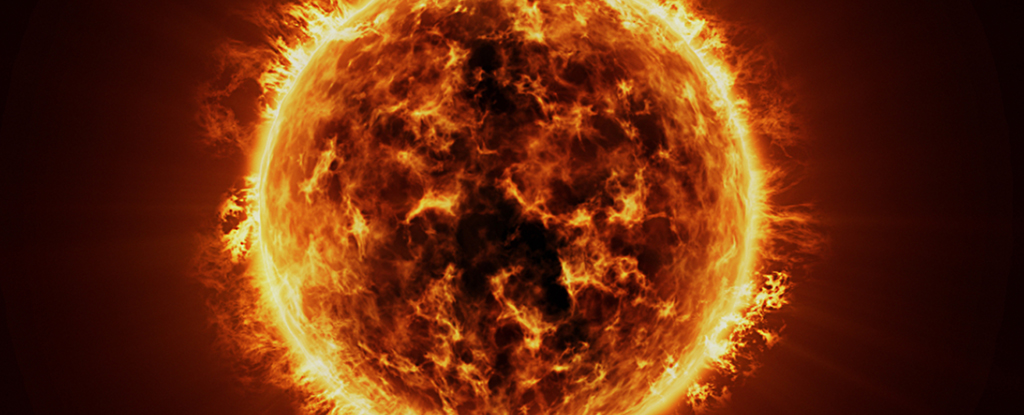

The team behind the Experimental Advanced Superconducting Tokamak (EAST) in China kept their fusion drive running for more than 1,000 seconds for the first time – lasting for 1,066 seconds (almost 18 minutes) to be exact.
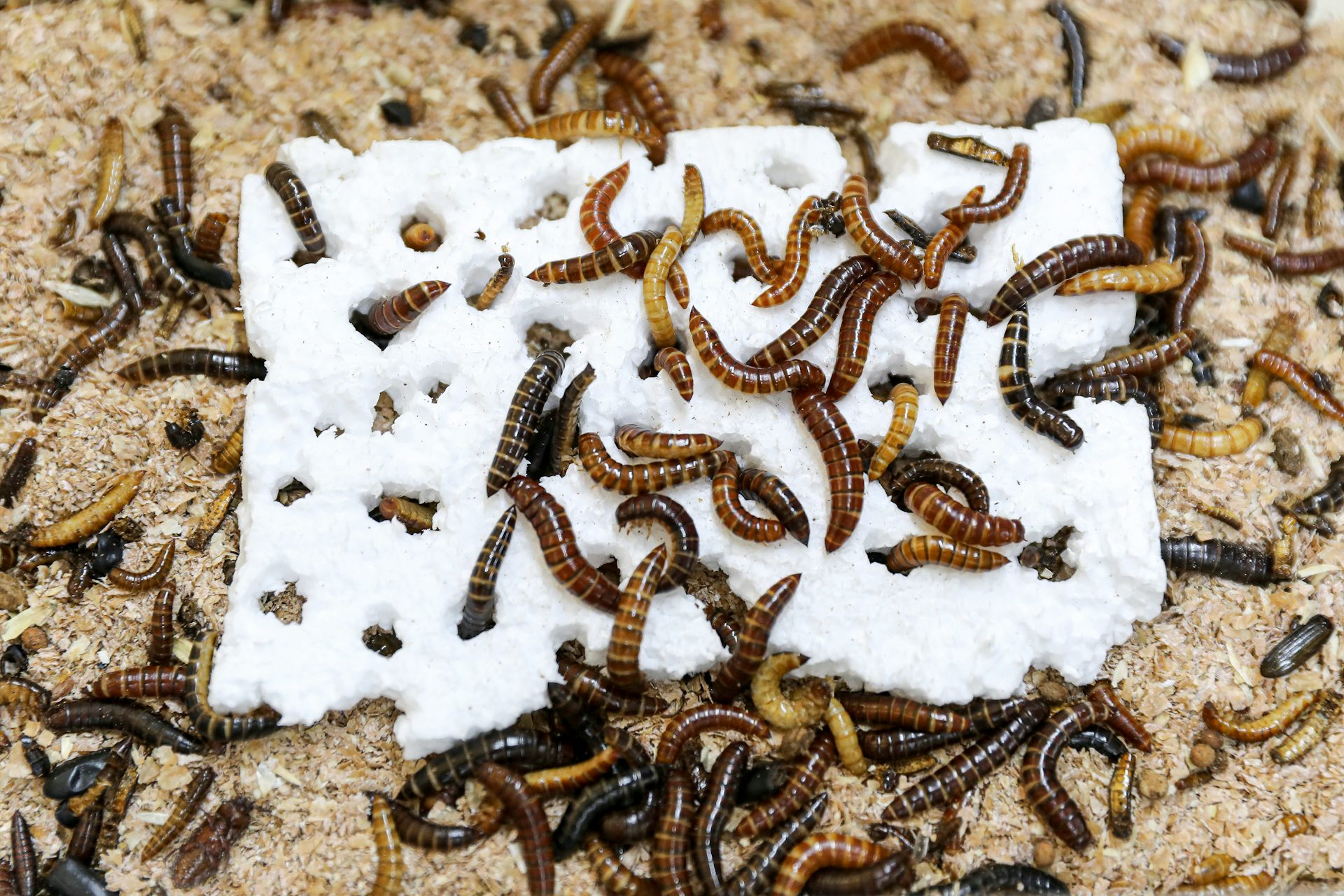

There’s been an exciting new discovery in the fight against plastic pollution: mealworm larvae that are capable of consuming polystyrene.

Proof clones can reproduce safely is key to restoration of severely endangered ferrets and other species, experts say.

Geckos use the saccule - a part of their inner ear traditionally associated with maintaining balance and body positioning - to detect low-frequency vibrations, according to a duo of biologists.
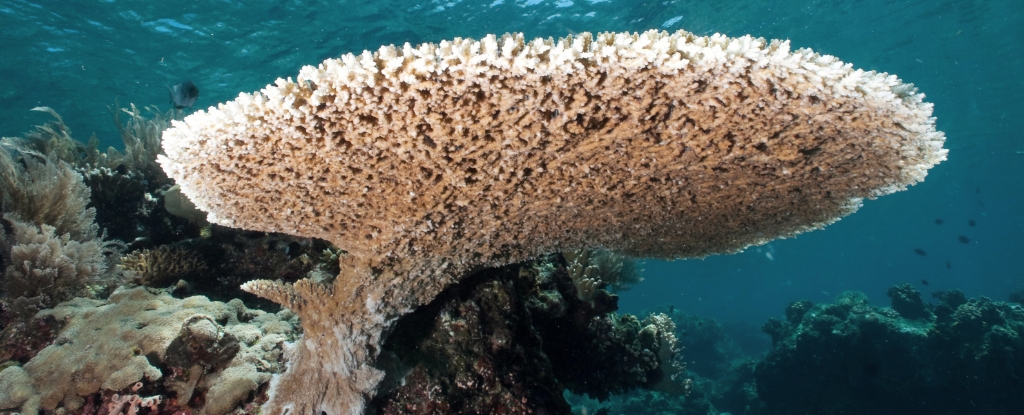

Surprising new evidence of variable heat tolerance in corals was discovered recently. As the world's oceans warm, these differences are important.