
A newly-discovered peatland in the Congo Basin of central Africa contains an estimated 30.6 billion tons of carbon in its waterlogged soils - equivalent to three times the total annual carbon emissions of every human being alive today.

Scientists have demonstrated the ability to 'see' the future of quantum systems and used that knowledge to preempt their demise, in a major achievement that could help bring the strange and powerful world of quantum technology closer to reality.

Scientists at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have discovered a protein that fine-tunes the cellular clock involved in aging.

A San Francisco, US - led study has identified signatures of ethnicity in the genome that appear to reflect an ethnic group's shared culture and environment, rather than their common genetic ancestry.

Porous, 3-D forms of graphene developed at MIT can be 10 times as strong as steel but much lighter.
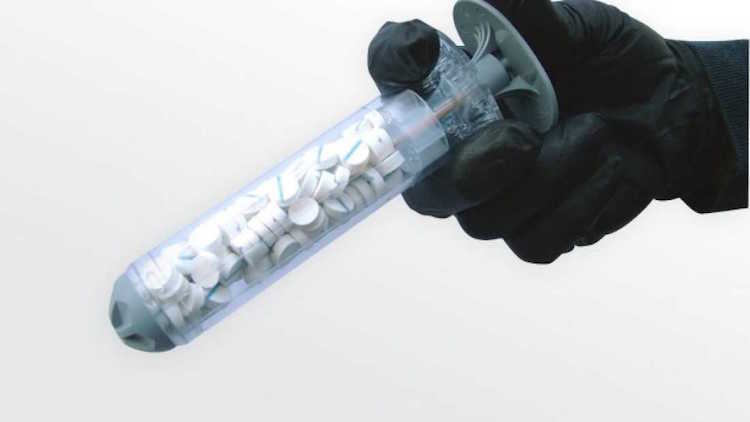
The XSTAT injector is in its final stages of approval and it has the ability to save thousands of lives from blood loss.

For more than a century, doctors have regarded the folds of flesh that hold our intestines in place as snippets of an elaborate support structure. Yet a pair of Irish researchers found that it’s actually one continuous fatty membrane, possibly constituting a whole new functional organ: the mesentery.

Scientists from the Dental Institute at King's College London have proven a way to stimulate the stem cells contained in the pulp of the tooth and generate new dentine in large cavities, potentially reducing the need for fillings or cements.

Physicists have performed a variation of the famous 200-year-old double-slit experiment that, for the first time, involves "exotic looped trajectories" of photons.

Of all the potentially apocalyptic technologies scientists have come up with in recent years, the gene drive is easily one of the most terrifying. But like most great risks, the gene drive also offers incredible reward.

Researchers have made the world's smallest radio receiver - built out of an assembly of atomic-scale defects in pink diamonds.

Scientists of the University Hospital Erlangen gained substantial knowledge of human dendritic cells, which might contribute to the development of immune therapies in the future.

More than 100,000 people participated in the BIG Bell Test, a global experiment to test the laws of quantum physics.

The CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technique has been used in its first human trial. Scientists at Sichuan University in Chengdu, China began a trial last month to treat a lung cancer patient.

MIT researchers discover astonishing behavior of water confined in carbon nanotubes.