
We are experiencing a new wave of innovation in health care - one that promises to create the smartest, most connected, and most efficient health systems the world has ever seen.

Today, much has changed when it comes to metals and materials in general, but one thing remains the same: It's advancement in this industry that drives innovations and breakthroughs everywhere else.

Basic physics suggests that electrons are essentially immortal. A fascinating experiment recently failed to overthrow this fundamental assumption.

How tiny can a computer get and what can it do? Digital sensors are already traveling inside human bodies. Will shrinking sizes eventually do away with the bulky devices we use now?

New collisions could help explain what conditions were like up to a billionth of a second after the Big Bang

Scientists say 3D-printed structures loaded with embryonic stem cells could one day help doctors print out micro-organs for transplant patients.

Physicists have used photons to communicate between two electrons through 1.2 miles of fiber optic cable.

Magnetic sensors are in everything from home appliances to car-counters at the drive-through. A new technology promises to make them cheaper and smaller.

Quantum entanglement - the process though which particle's states become inextricably linked, despite being nowhere near each other, is usually carried out at incredibly low temperatures. But not any more: now physicists can perform the act at room temperature, which could have a profound effect on quantum computing and security.

Researchers from the Centre for Quantum Technologies (CQT) at the National University of Singapore and the University of Seville in Spain have reported the most extreme 'entanglement' between pairs of photons ever seen in the lab.

Scientists at Queen's University Belfast have made a major breakthrough by making a porous liquid - with the potential for a massive range of new technologies including 'carbon capture'.

The first measurement of the interaction between antiprotons - the antimatter equivalent of protons - has been completed by an international team of physicists working at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) at Brookhaven National Laboratory in New York.
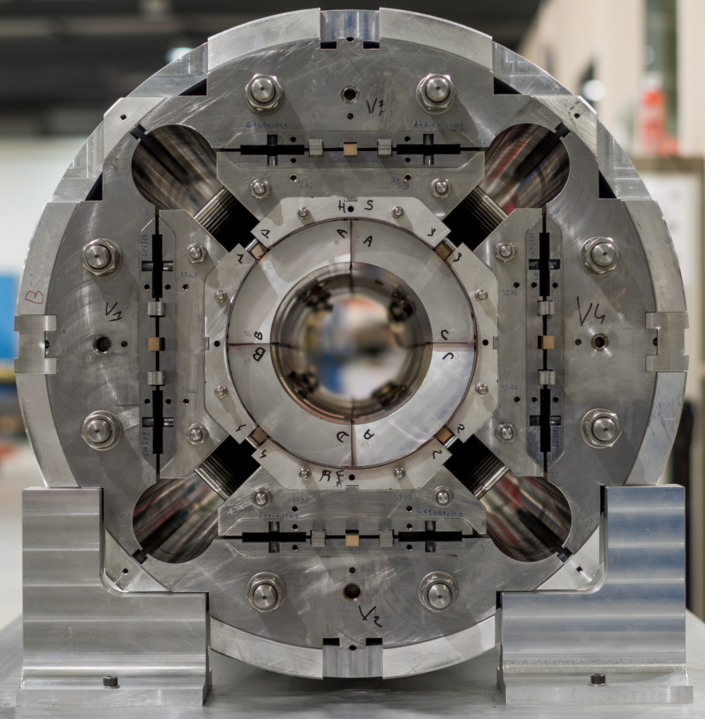
China's Circular Electron Positron Collider (CEPC) is expected to be at least twice the size of the world's current leading collider, the Large Hadron Collider.

With this leukemia reversal, gene editing has now demonstrated remarkable promise and fueled optimism about future uses. But experts urge caution.

New research uncovers an unusual form of matter - not a conventional metal, insulator, or magnet, for example, but something entirely different.