
A 3,000 kilometer thick layer of hot compressed rock sandwiched between Earth

Physicists have now provided the first major results of NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) mission, including an unprecedented look at the interaction between the magnetic fields of Earth and the sun.

When we published a paper in 2013 finding 97% scientific consensus on human-caused global warming, what surprised me was how surprised everyone was. Ours wasn't the first study to find such a scientific consensus. Nor was it the second. Nor were we the last.

Peabody Energy, the world’s largest coal producer, filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy Wednesday, the latest casualty in an industry that has been shaken by the recent shale gas boom, climate change policy and economics that greatly disfavor coal production.
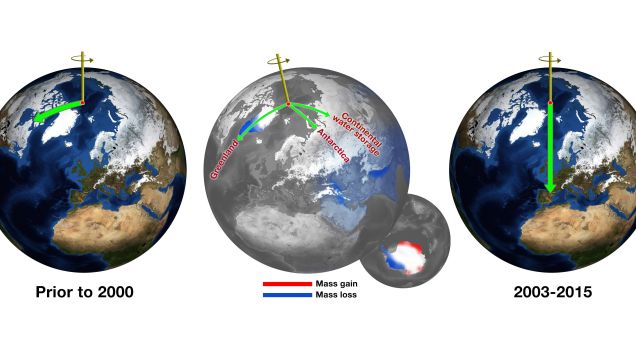
Something strange is happening to our planet. Around the year 2000, the North rotational pole started migrating eastward at a vigorous clip. Now, scientists at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory have figured out what's going on, and you'll be shocked to learn that humans are behind it.

"It's a practical possibility," says biologist E.O. Wilson, and it could save 80 to 90 percent of all species on Earth.

The impact humans have made on Earth in terms of how we produce and consume resources has formed a 'striking new pattern' in the planet's global energy flow, according to researchers.

Earth is home to 2,550 exotic minerals, some so scarce the world supply would fit inside a sugar cube. One of the Earth’s rarest minerals is Nevadaite, which has only been found in two places on the planet.
A new research has suggested that Planets Similar to Earth Have Identical Interiors.

From Lunar orbit, Earth is obviously habitable. But from a distant point in the galaxy, not so much.

A new study suggests that plate tectonics -- the dynamic processes that formed Earth's mountains, volcanoes and continents -- began about 3 billion years ago. By analyzing trace element ratios that correlate to magnesium content in ancient Earth's crust, the researchers provide first-order geochemical evidence for when plate tectonics first got underway.

NASA announced the creation of the Planetary Defense Coordination Office on Thursday. Pictured are orbits of near-Earth asteroids (blue) and potentially hazardous asteroids (orange).

A deal to attempt to limit the rise in global temperatures to less than 2C has been agreed at the climate change summit in Paris.

Some of the five mass extinctions Earth experienced in the past were driven by climate changes. Future Earth will be just fine.

Some want to scrap adjustment that keeps atomic time in sync with Earth