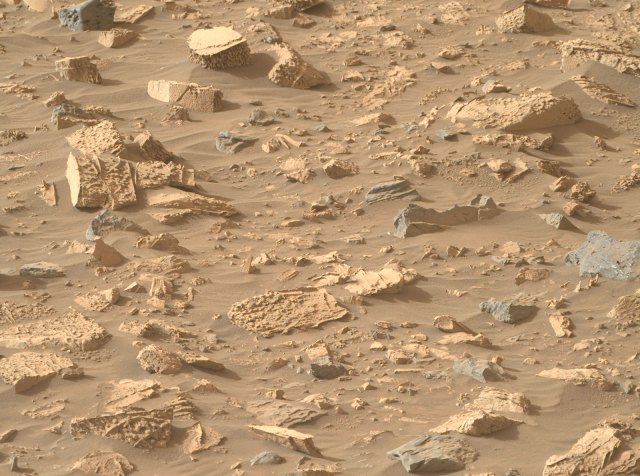

After months of driving, Perseverance has finally arrived at "Bright Angel", discovering oddly textured rock unlike any the rover has seen before.
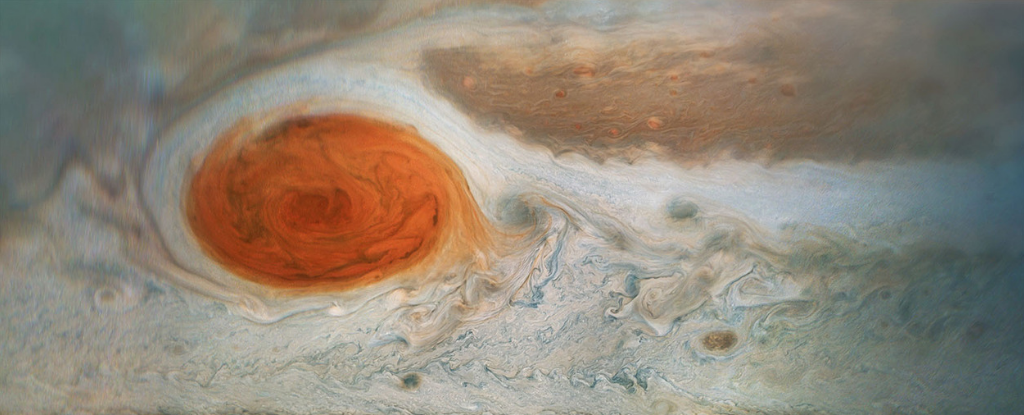

Jupiter's Great Red Spot (GRS) is one of the Solar System's defining features. It's a massive storm that astronomers have observed since the 1600s. However, its date of formation and longevity are up for debate.

In addition to producing auroras, a recent extreme storm provided more detail on how much radiation future astronauts could encounter on the Red Planet.
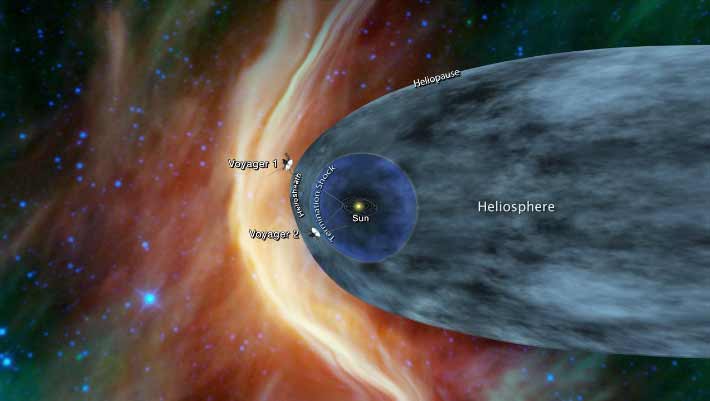
Cold, dense clouds in the interstellar medium of our Milky Way Galaxy are around four-five orders of magnitude denser than their diffuse counterparts.
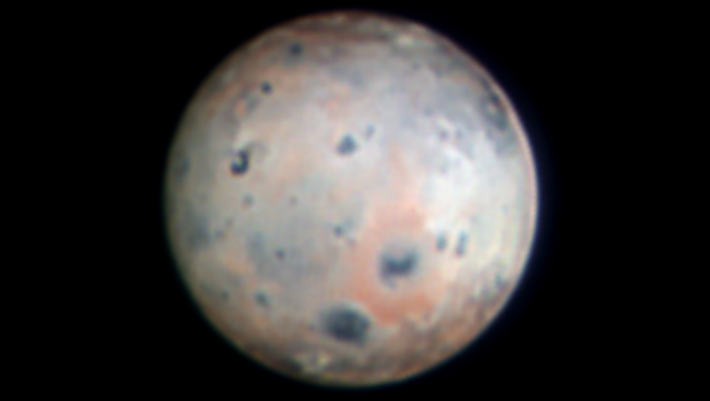

Using the SHARK-VIS instrument on the Large Binocular Telescope on Mount Graham in Arizona, the United States, astronomers have captured the highest resolution optical images of Io ever obtained from a ground-based telescope.
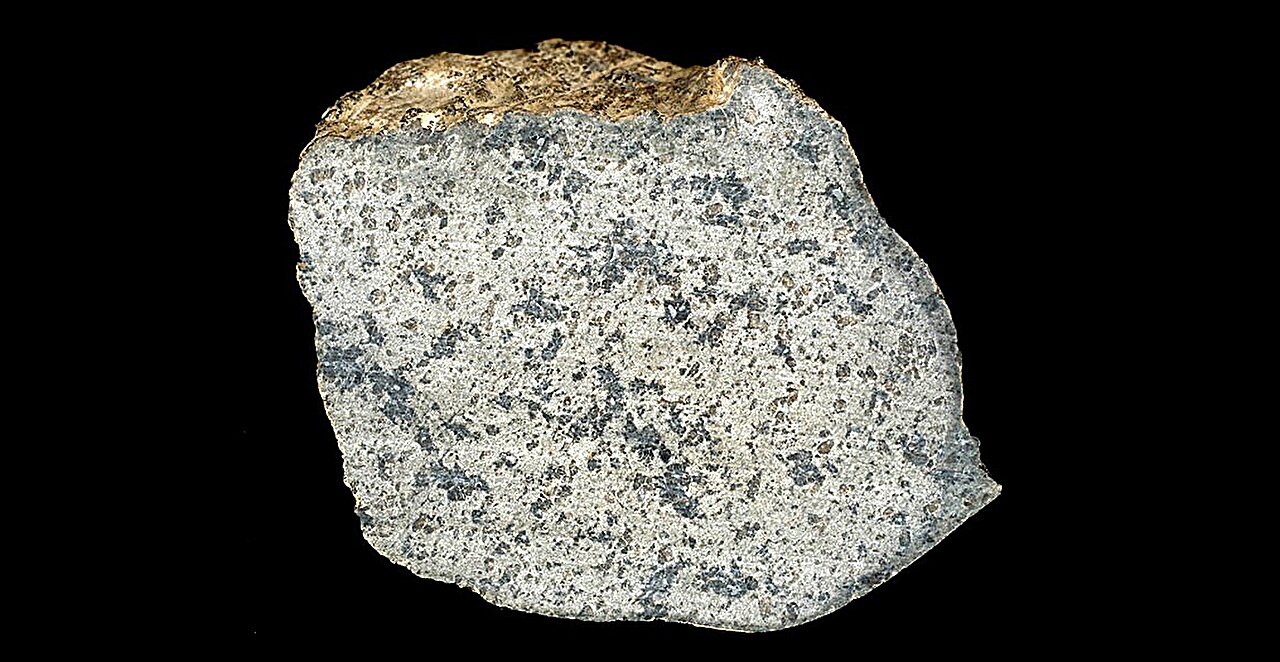

Mars has a distinct structure in its mantle and crust with discernible reservoirs, and this is known thanks to meteorites that scientists have analyzed.
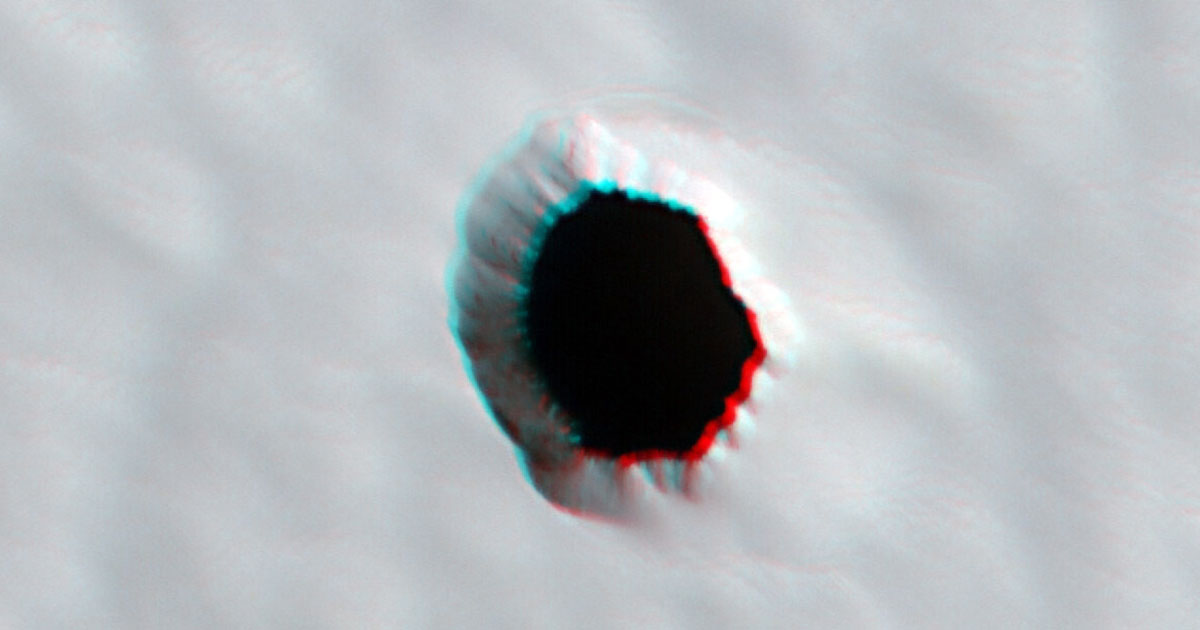

NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) has discovered another intriguing formation on the planet's barren surface. Despite their best efforts, scientists can only guess as to how exactly holes like this one were formed.
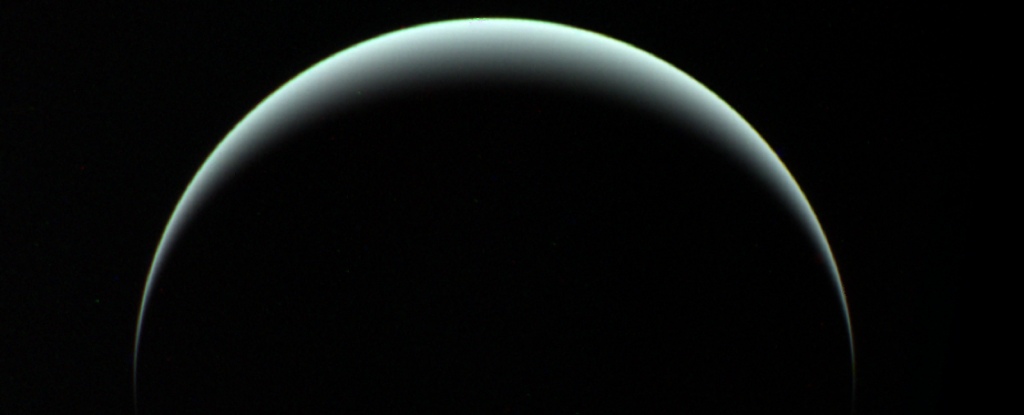

One of the most peculiar things about Uranus and Neptune is their magnetic fields.
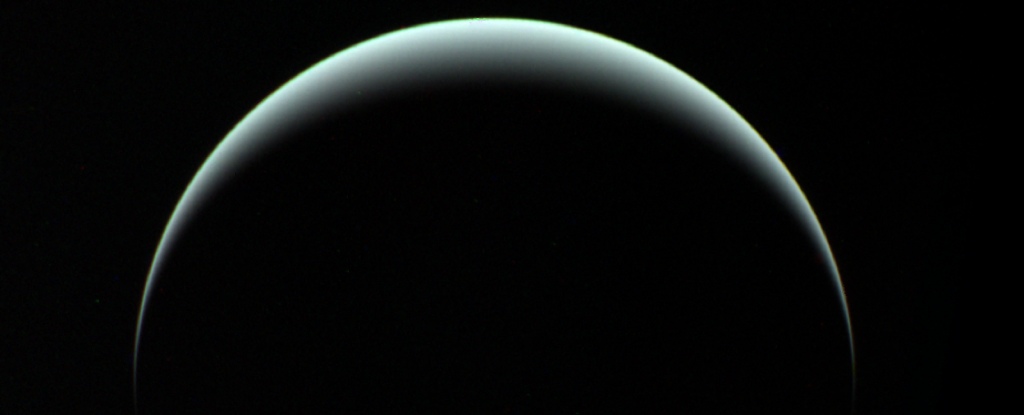

One of the most peculiar things about Uranus and Neptune is their magnetic fields.
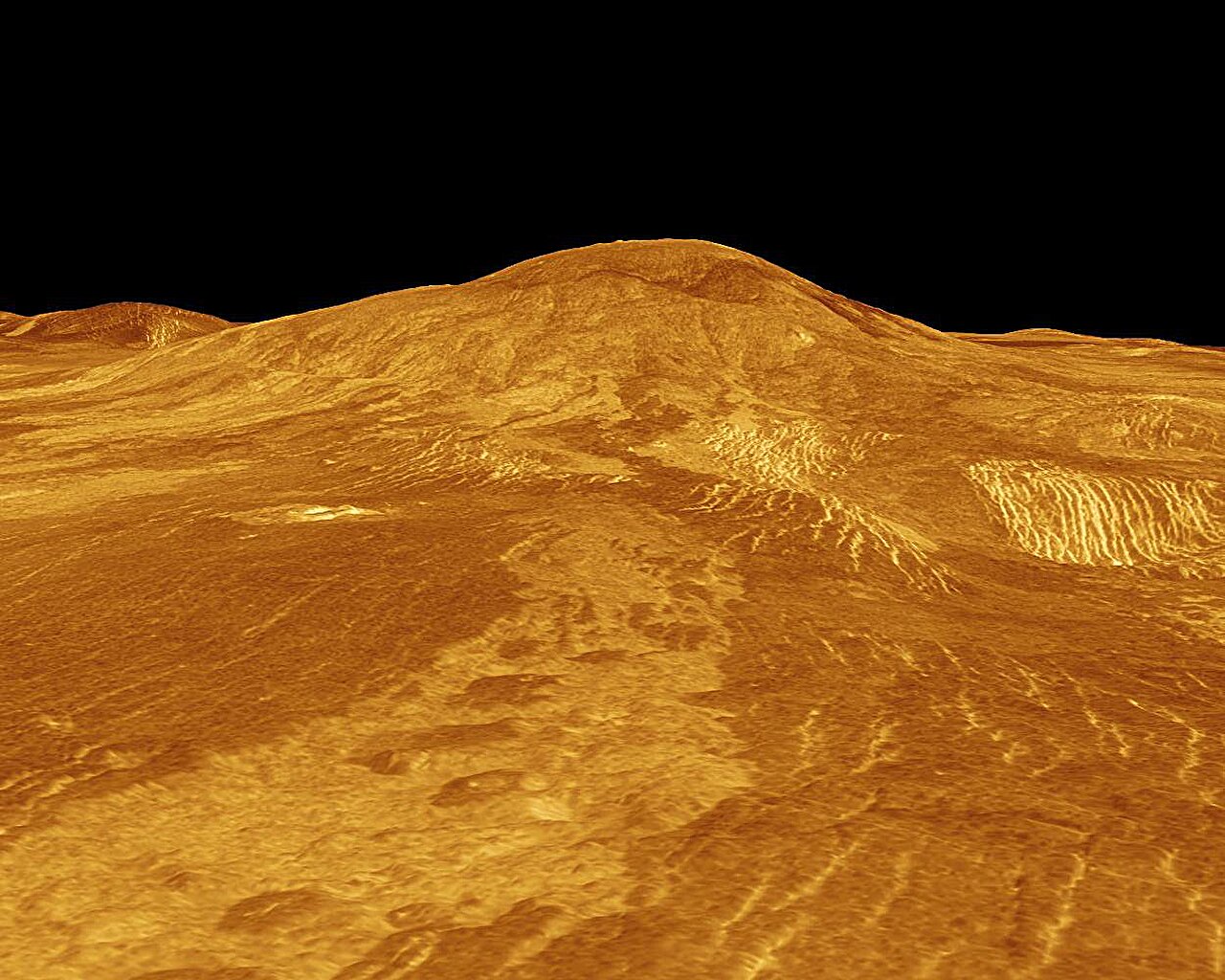
A new analysis of data collected on Venus more than 30 years ago suggests the planet may currently be volcanically active.

Six of the planets of the Solar System are about to line up for a rare sight in Earth's sky.
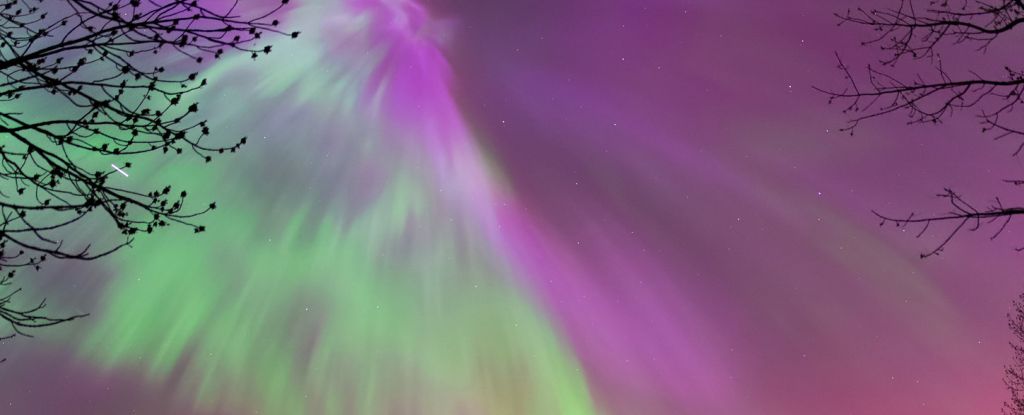

A solar storm that filled Earth's skies with shimmering curtains of light in May 2024 was so intense that its effects were felt, even at the bottom of the ocean.

Nasa says its Perseverance rover has essentially completed the job it was asked to do when it landed on Mars in February 2021.
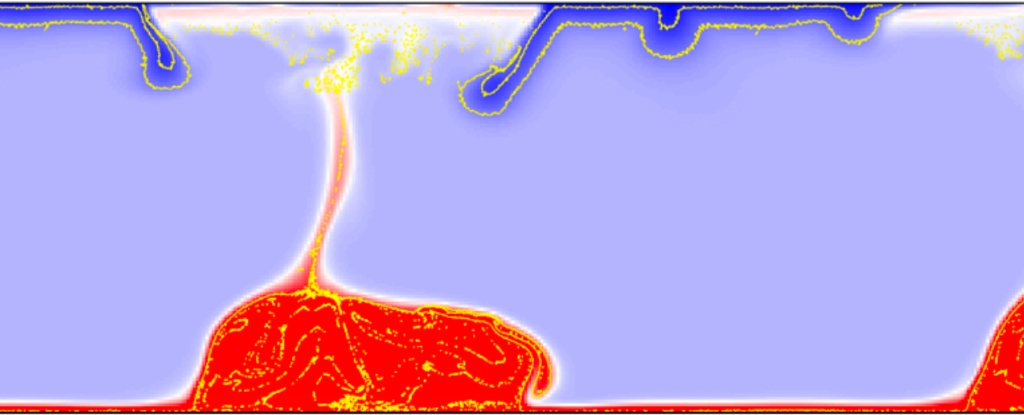
On the scale of cataclysmic events, the whomping impact of a Mars-sized object that crashed into Earth some 4.5 billion years ago ranks pretty highly: thought to have set in motion the movement of our planet's fractured, rocky crust.

A new study details dissociative recombination, which may have led to Venus losing its water.