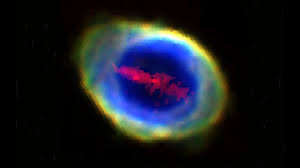
A mysterious bar-shaped cloud of iron has been discovered inside the iconic Ring Nebula.
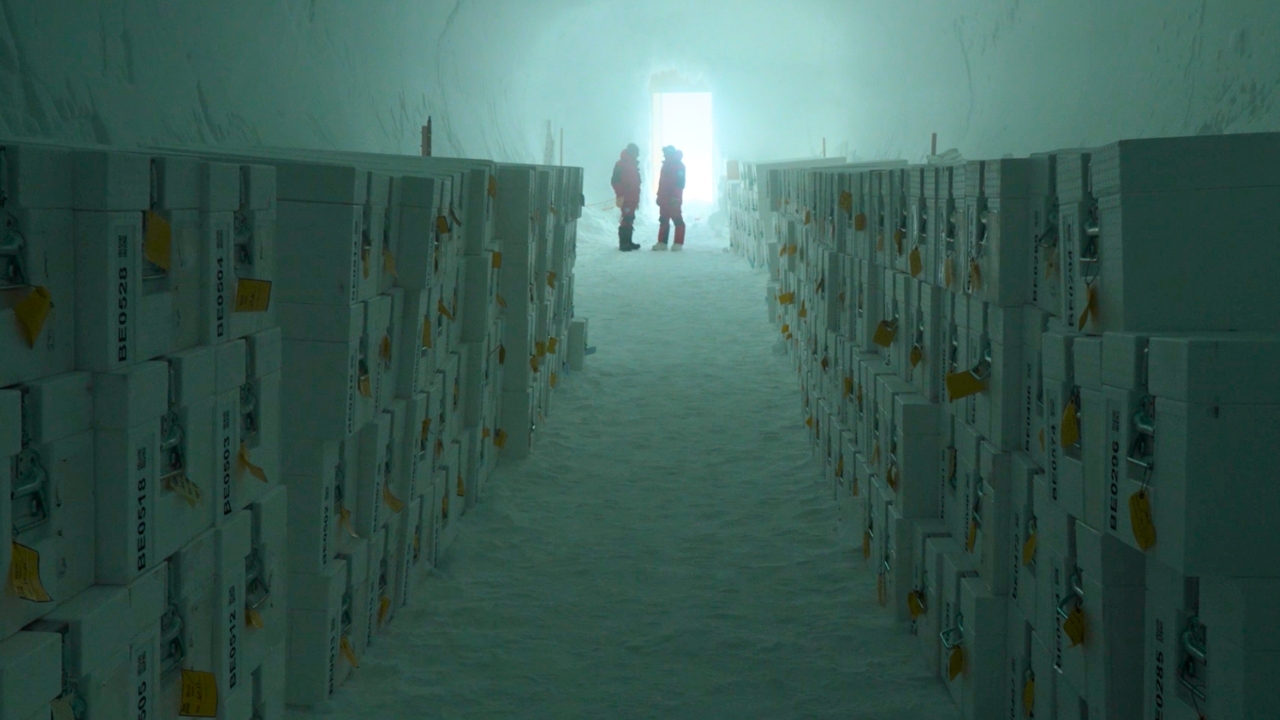

Scientists on Wednesday sealed ancient chunks of glacial ice in a first-of-its-kind sanctuary in Antarctica in the hope of preserving these fast-disappearing records of Earth's past climate for centuries to come.
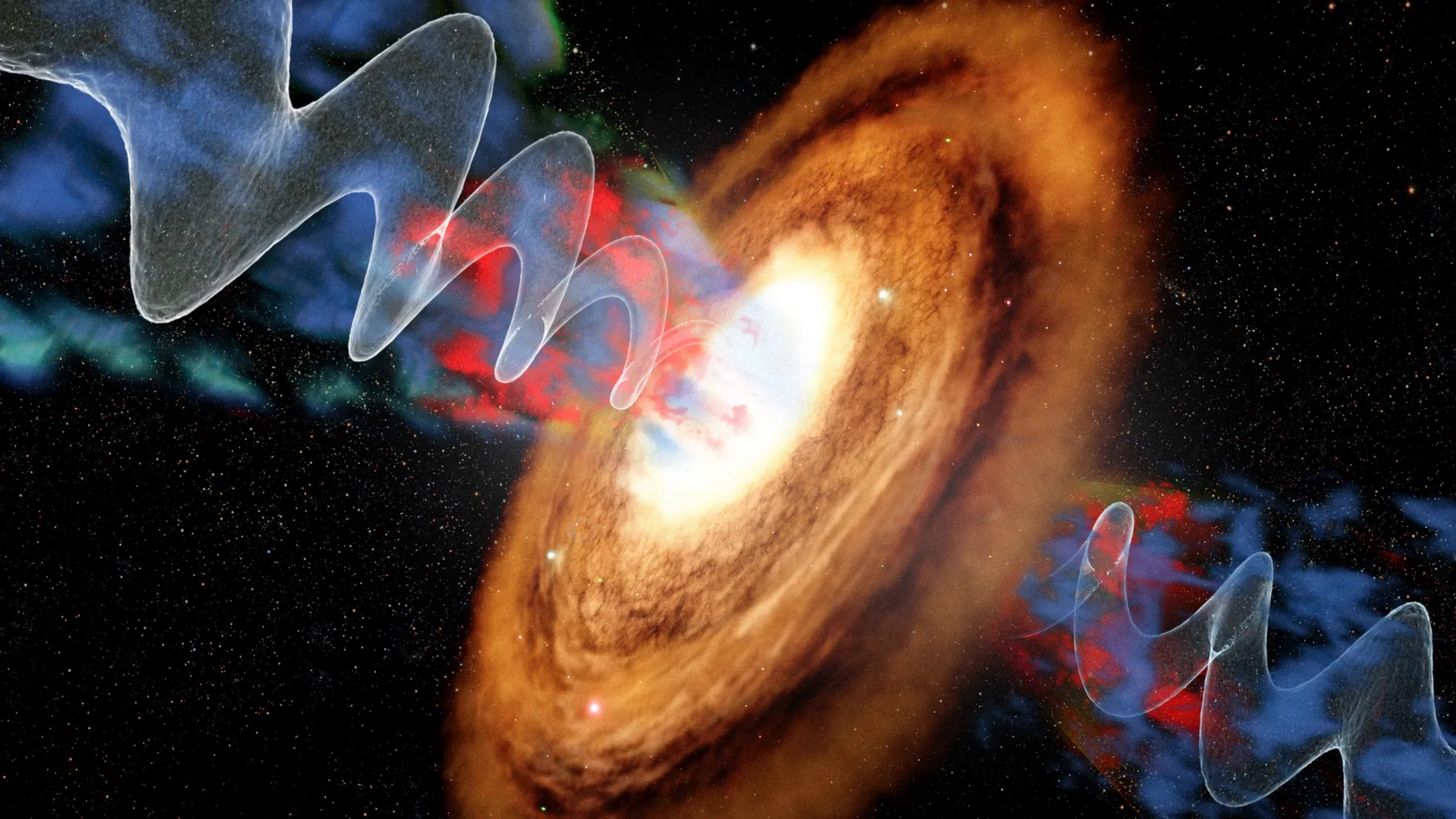

A nearby active galaxy called VV 340a offers a dramatic look at how a supermassive black hole can reshape its entire host.
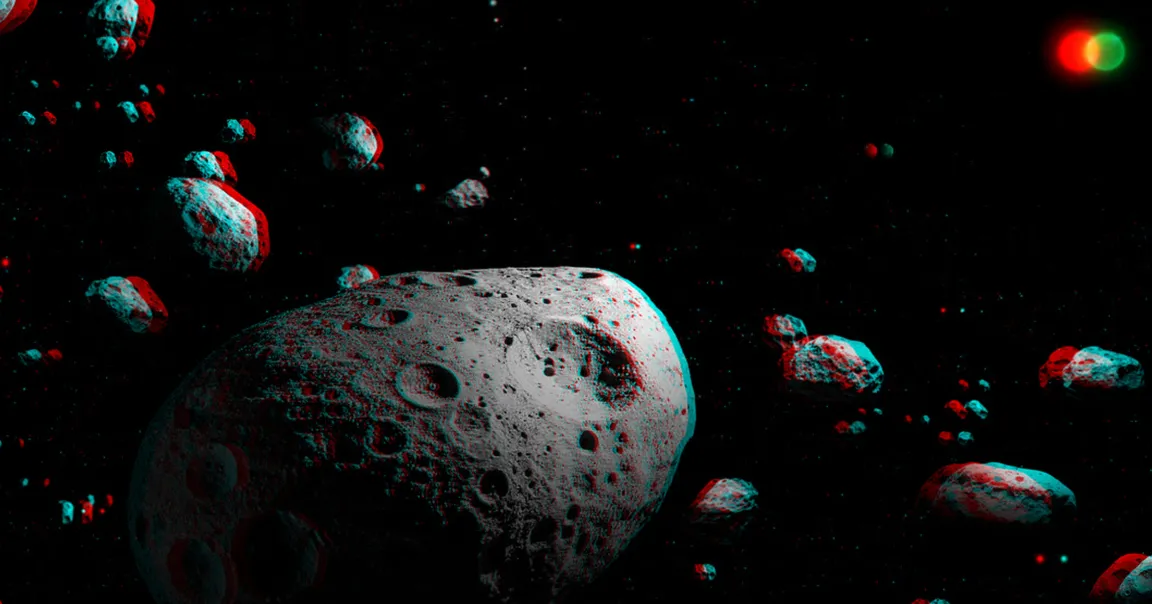

The unusual cosmic lump — dubbed 2025 MN45, 2,300 feet in diameter and located in the Main Asteroid Belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter — completes a full rotation every minute and 53 seconds.
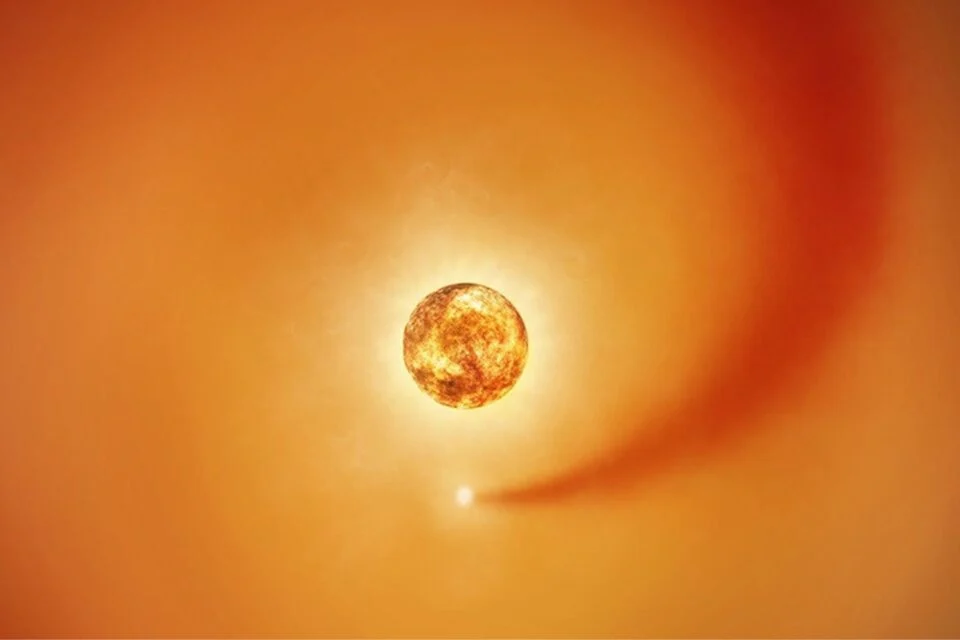
Astronomers observed changes in the star’s spectrum and these changes are the direct result of the companion star, Siwarha, plowing through Betelgeuse’s outer atmosphere.

A team of astronomers discovered an extremely hot galaxy cluster that’s far hotter and older than current theories allow.

An object spotted in deep space is the strongest candidate yet for a galaxy arrested during early development.
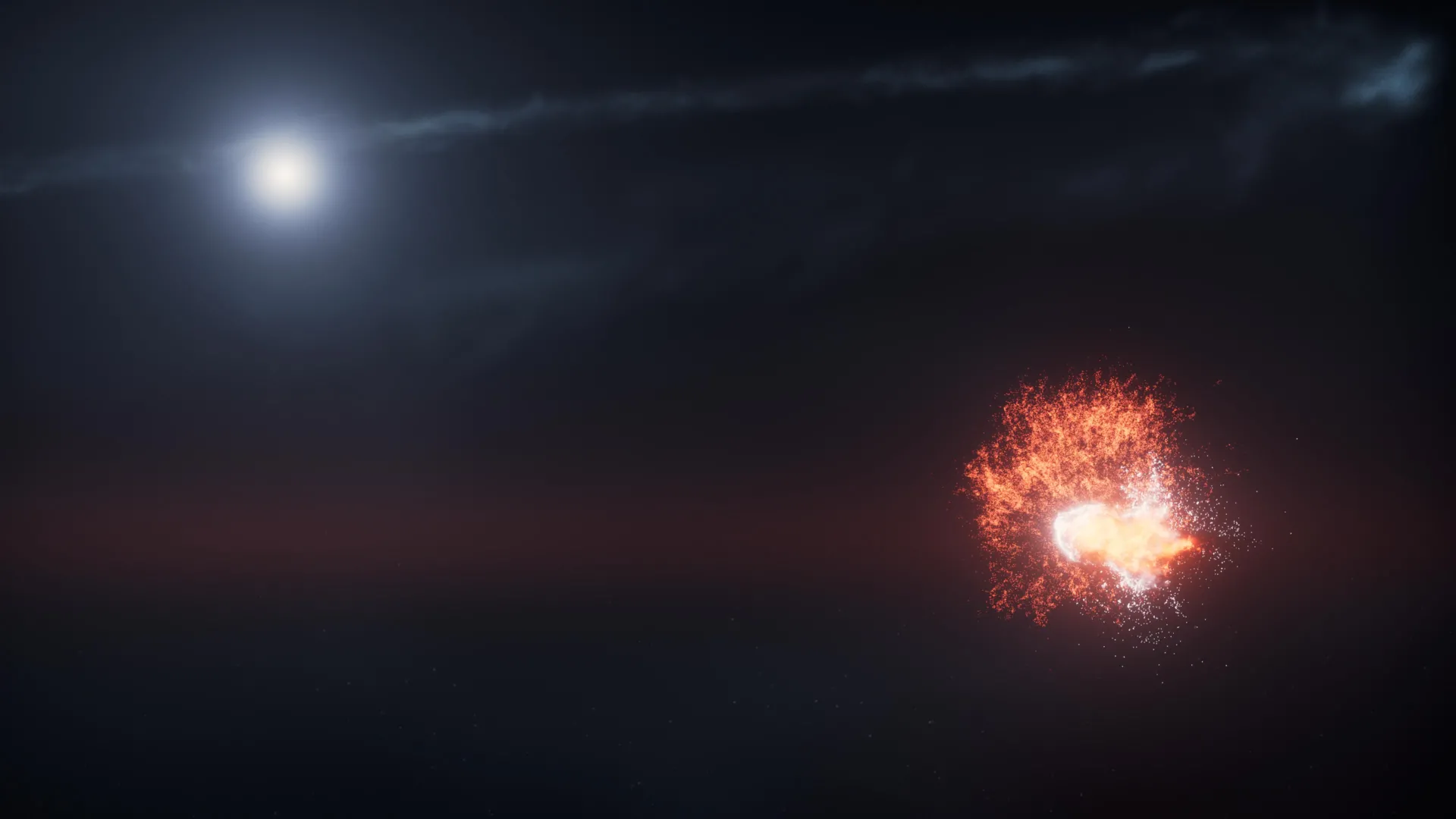

Astronomers tracking a nearby star system thought they had spotted an exoplanet reflecting light from its star. Then it vanished. Even stranger, another bright object appeared nearby.
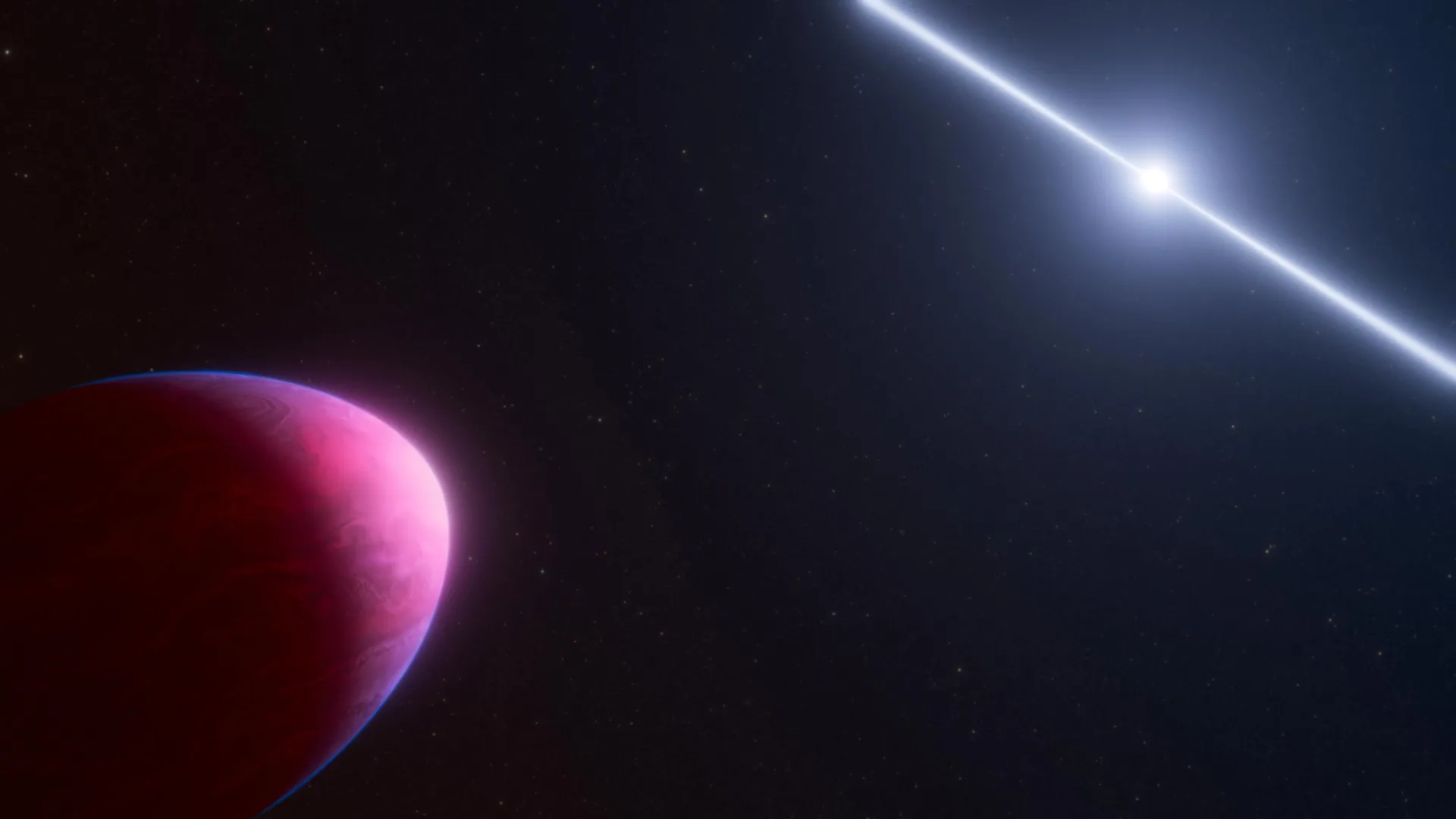

A newly discovered exoplanet is rewriting the rules of what planets can be. Orbiting a city-sized neutron star, this Jupiter-mass world has a bizarre carbon-rich atmosphere filled with soot clouds and possibly diamonds at its core.
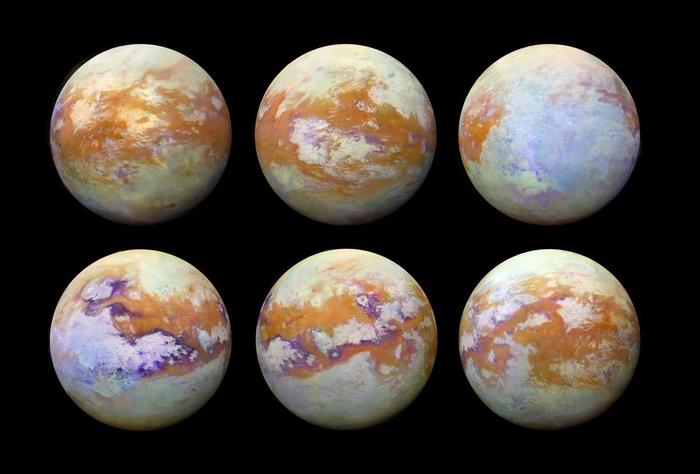

Careful reanalysis of data from more than a decade ago indicates that Saturn’s biggest moon, Titan, does not have a vast ocean beneath its icy surface, as suggested previously.
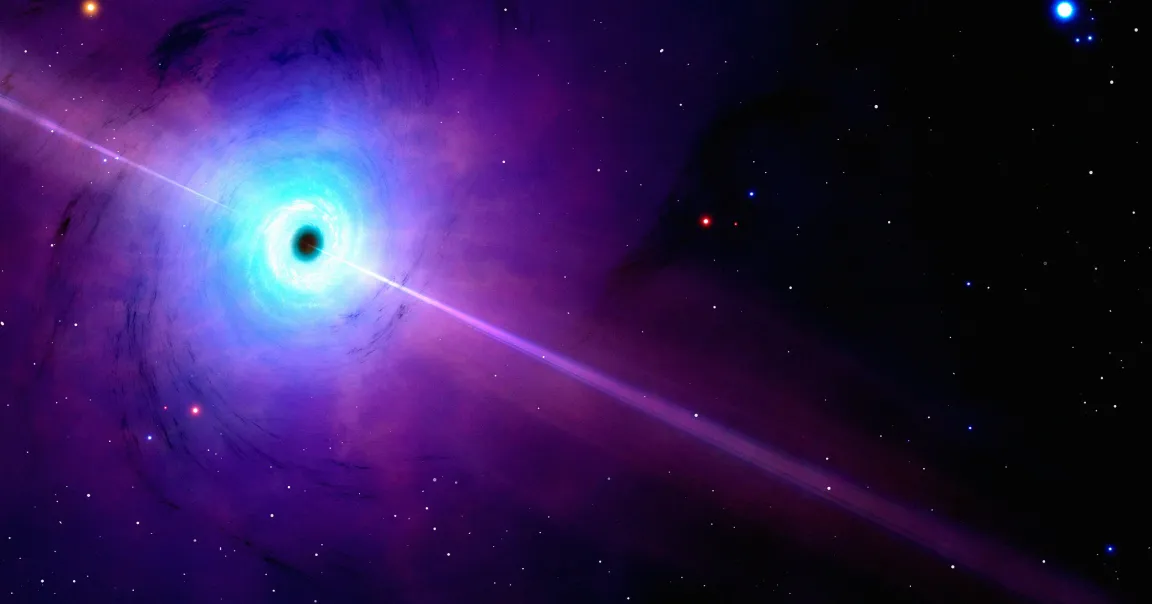

An international team of astronomers claim to have made a baffling discovery with the help of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope: the first runaway supermassive black hole that’s rocketing away from its home at a staggering speed.

Astronomers from the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA) and elsewhere report the discovery of a new brown dwarf about 60 times more massive than Jupiter.

Researchers using the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope have confirmed an actively growing supermassive black hole within a galaxy just 570 million years after the Big Bang.
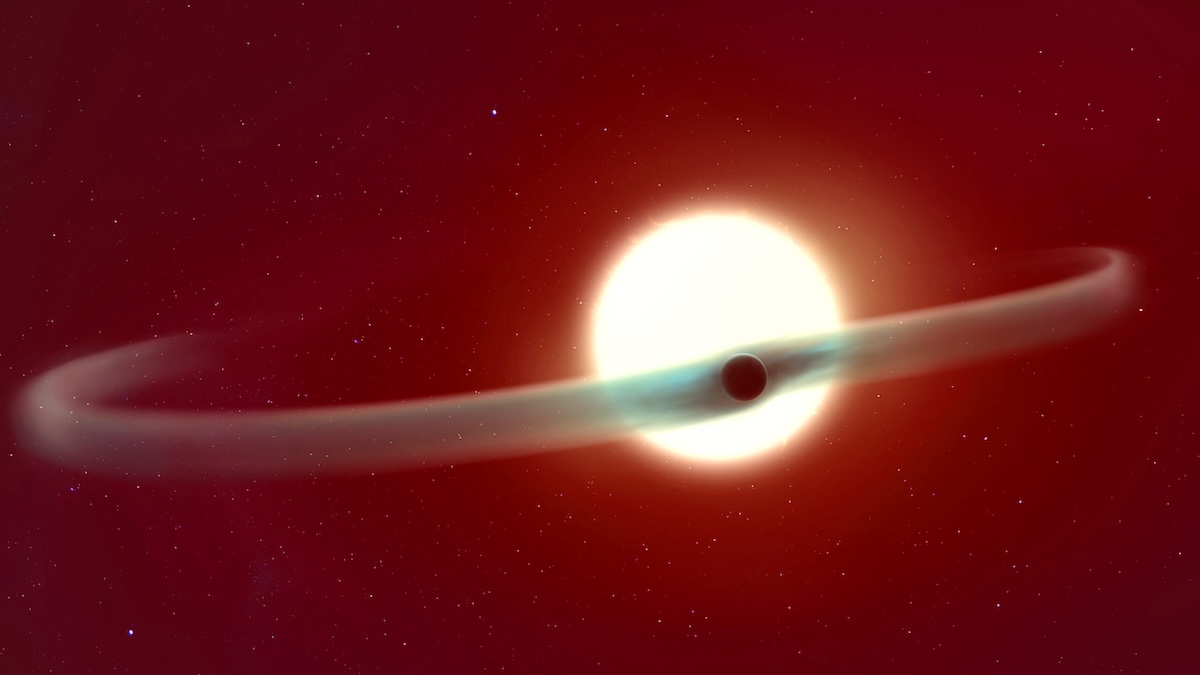

About 880 light-years from Earth, a hot mess of an exoplanet is slowly spilling its atmosphere into space, creating two enormous tails of helium that stretch more than halfway around its star.

A new Swiss-led study uses innovative hybrid modeling to reveal that these planets could just as easily be dominated by rock as by water-rich ices.