
Astronomers have found evidence for an intermediate-mass black hole in IRS 13, a population of dusty stellar objects within the nuclear star cluster of our Milky Way Galaxy.

Among several recent findings, the rover has found rocks made of pure sulfur — a first on the Red Planet.

A team of Italian researchers say they have discovered evidence of a lunar cave and suspect that there could be hundreds more.
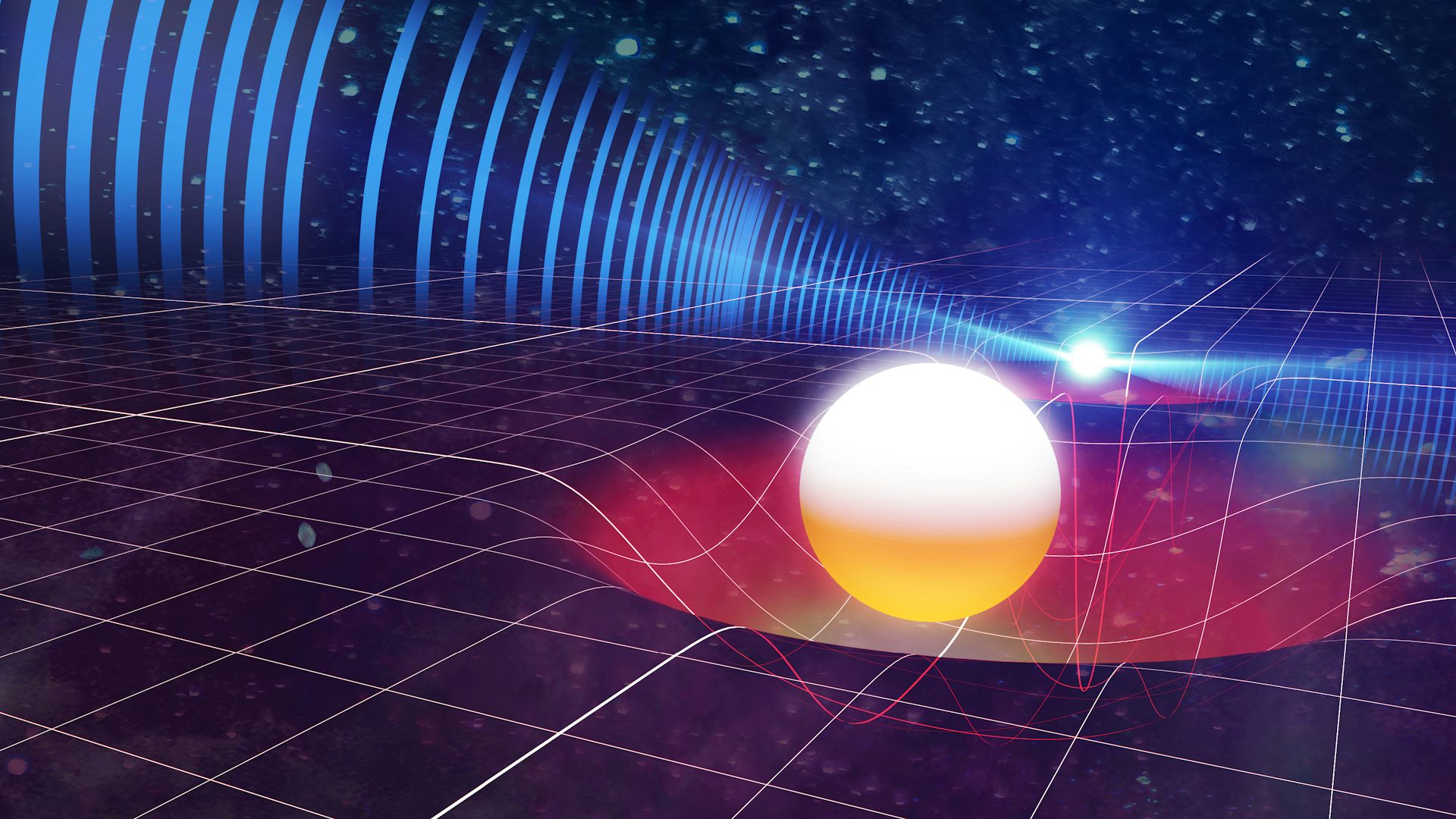
Neutron stars are some of the most extreme objects in the universe. Formed from the collapsed cores of supergiant stars, they weigh more than our Sun and yet are compressed into a sphere the size of a city.

An international team of astronomers has detected seven fast-moving stars in Omega Centauri region. These stars provide compelling new evidence for the presence of an intermediate-mass black hole.
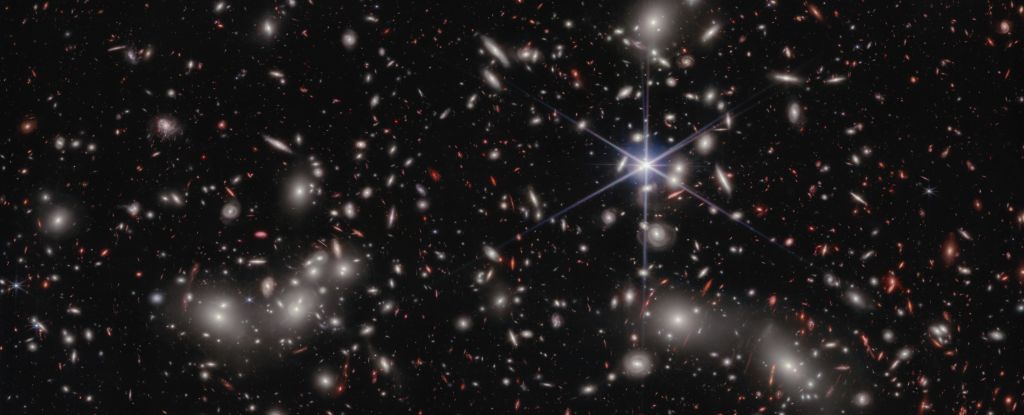

According to data from the Hubble and James Webb Space Telescopes, the origins of the free-flying photons in the early cosmic dawn were small dwarf galaxies that flared to life, clearing the fog of murky hydrogen that filled intergalactic space.
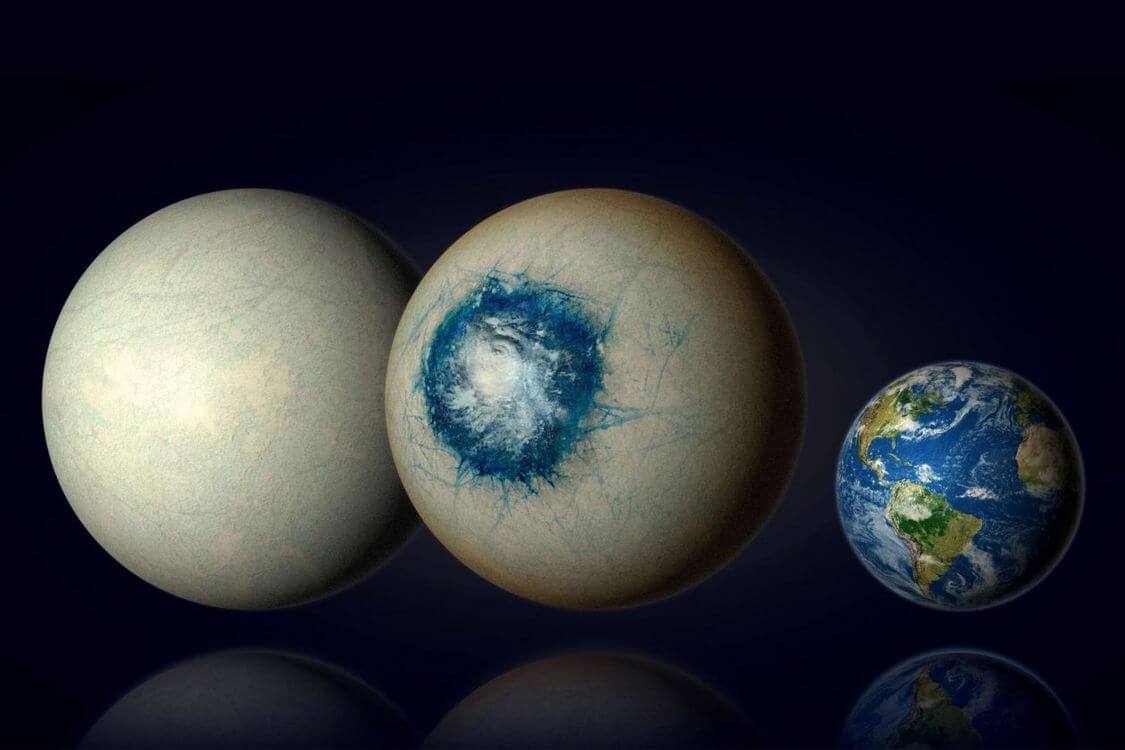
Researchers at the University of Montreal believe a vast ocean on exoplanet LHS 1140 b may be teeming with alien life.
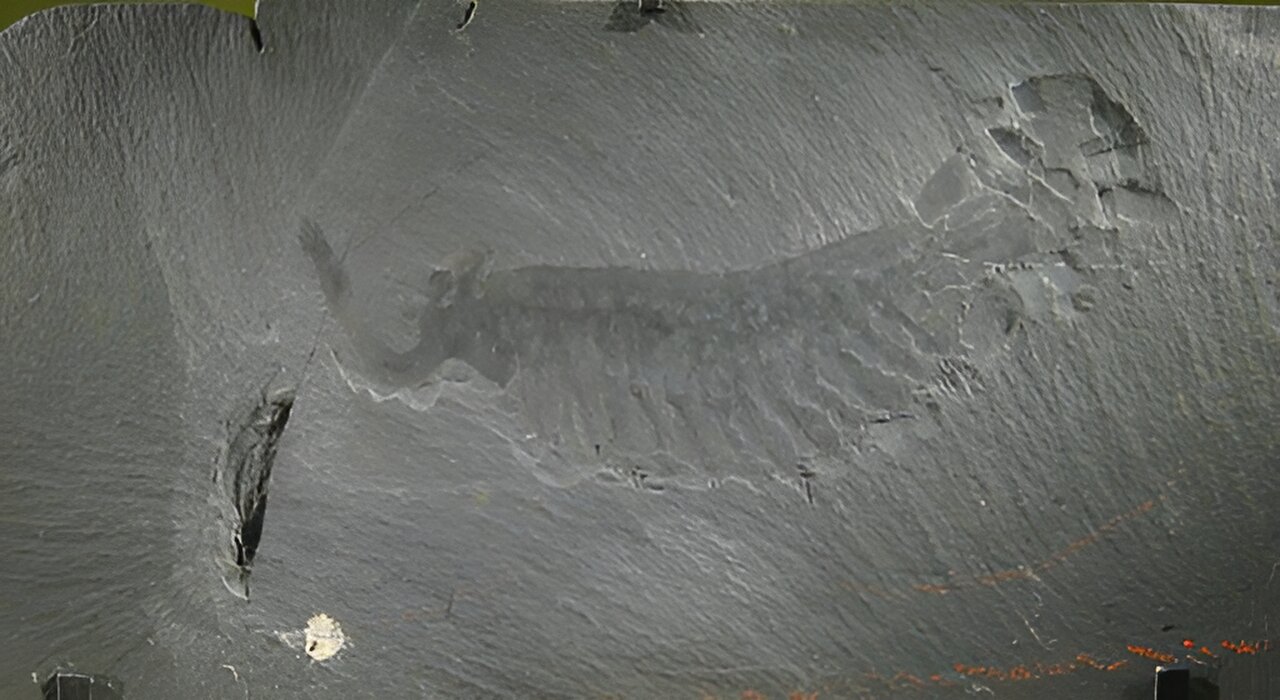

New research provides the clearest evidence yet that the Cambrian explosion - a rapid burst of evolution 540 million years ago, could have been triggered by only a small increase in oxygen levels in Earth's atmosphere and shallow ocean waters.
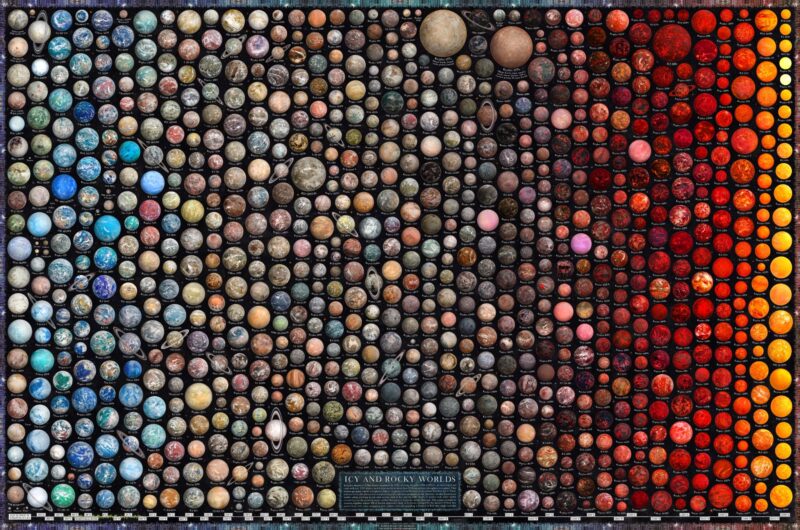

Martin Vargic illustrated more than 1,100 exoplanets based on astronomical discoveries. His art is a attempt to artistically visualize and compare thousands of exoplanets of all types and sizes according to observational data.
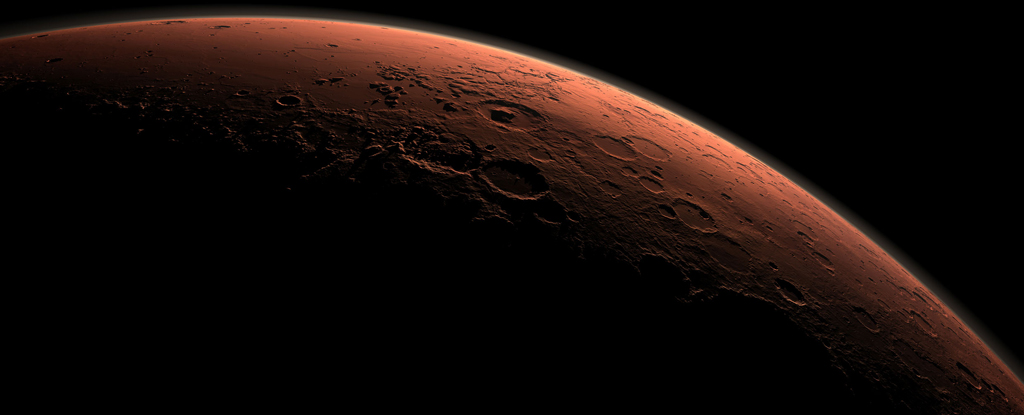
A team of researchers has uncovered evidence of its origins in the atmosphere, where carbon dioxide bathed in ultraviolet sunlight reacted to form a mist of carbon molecules that rained onto the planet's surface.
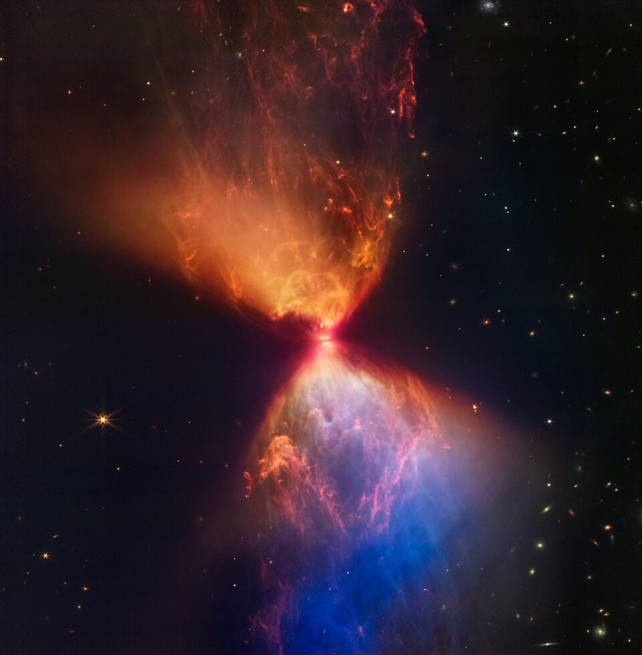

james Webb Space Telescope continues to revolutionise astronomy - it now shows the birth of a star. The star is named L1527, and at this young age, it's still ensconced in the molecular cloud that spawned it.
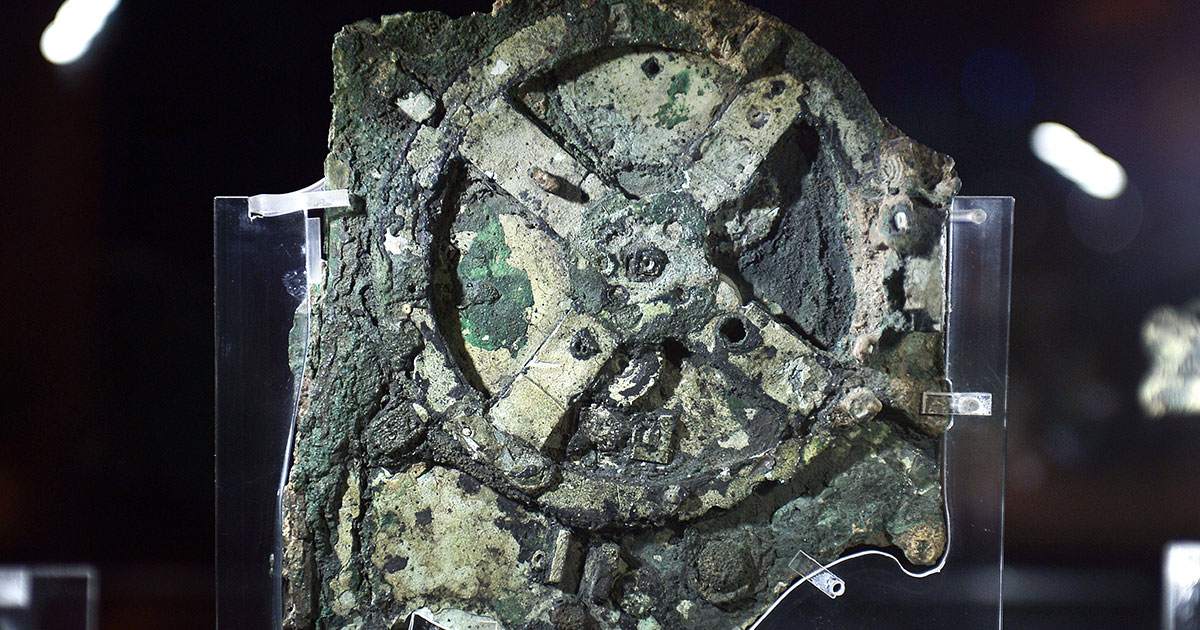

Researchers say they've used cutting-edge gravitational wave research to shed new light on a nearly 2,000-year-old mystery.
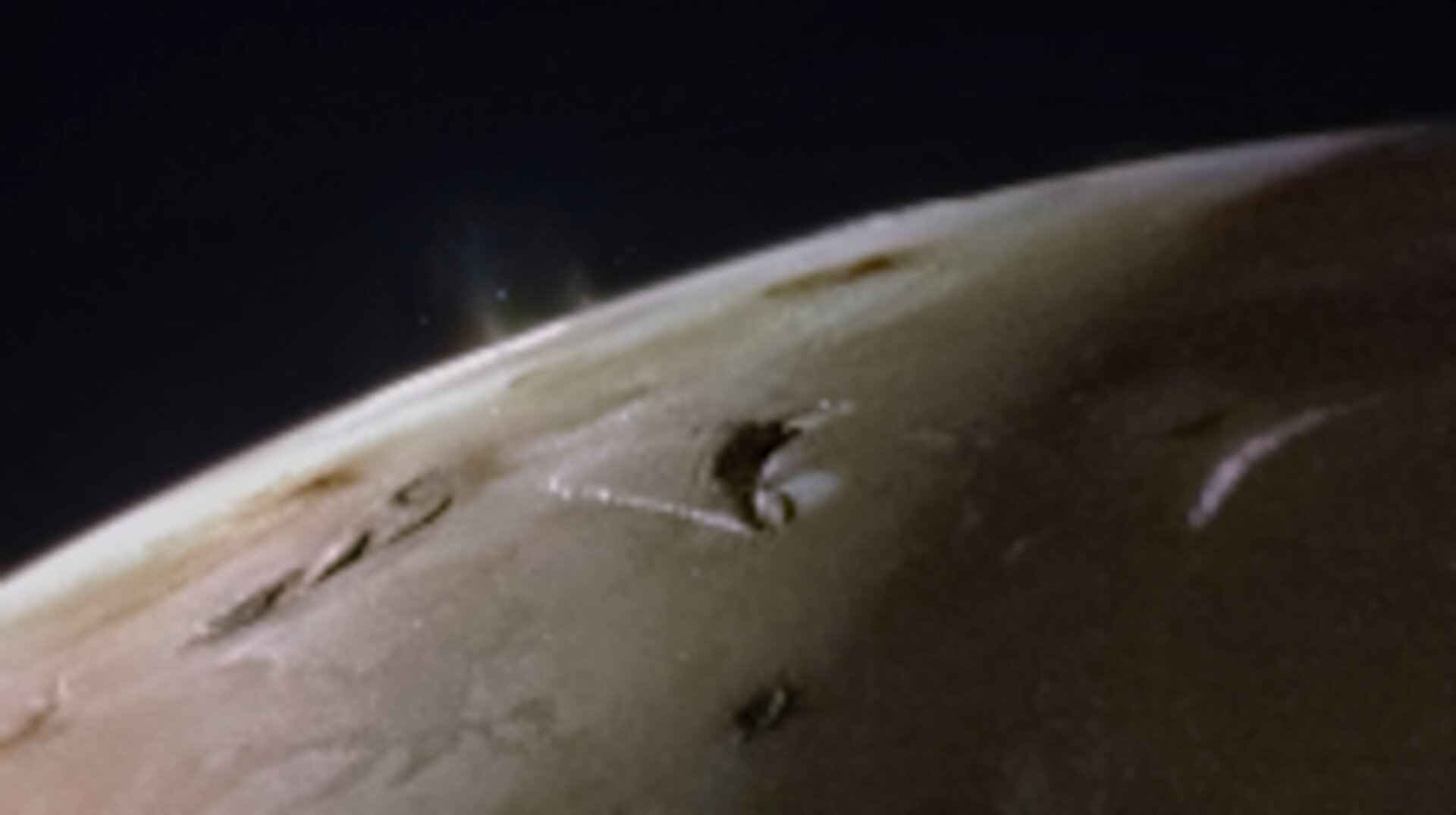

From around 2,400 miles away, the probe’s Jovian Infrared Auroral Mapper (JIRAM) instrument “revealed that the whole surface of Io is covered by lava lakes contained in caldera-like features.

The two new satellites, named Virgo III and Sextans II, were discovered in a region of space already crowded with more dwarf galaxies than models of dark matter predict.
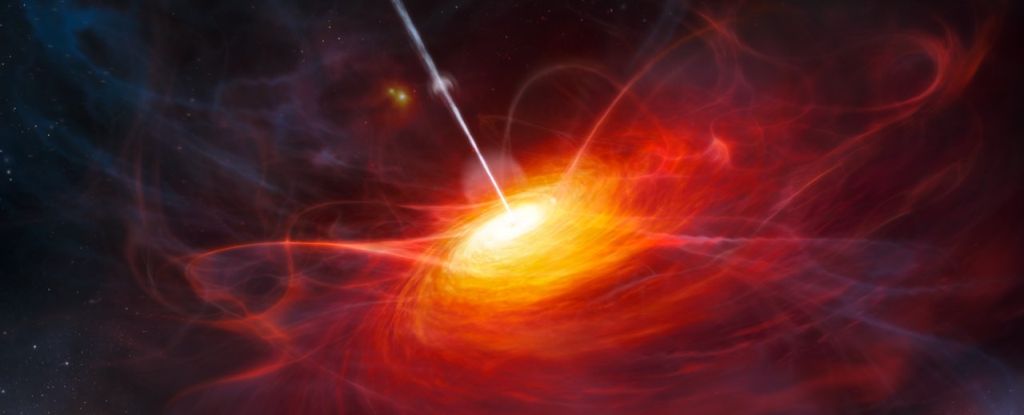

A black hole discovered lurking in the Cosmic Dawn is just way too big to easily explain.