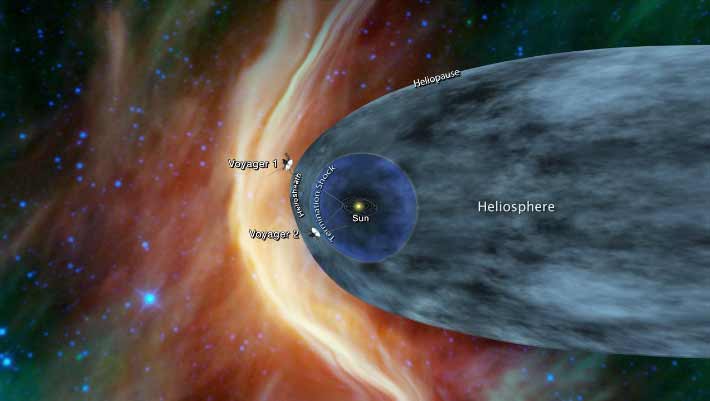
Cold, dense clouds in the interstellar medium of our Milky Way Galaxy are around four-five orders of magnitude denser than their diffuse counterparts.

Researchers have demonstrated the first chip-based 3D printer, a tiny device that emits reconfigurable beams of visible light into a well of resin that rapidly cures into a solid shape.
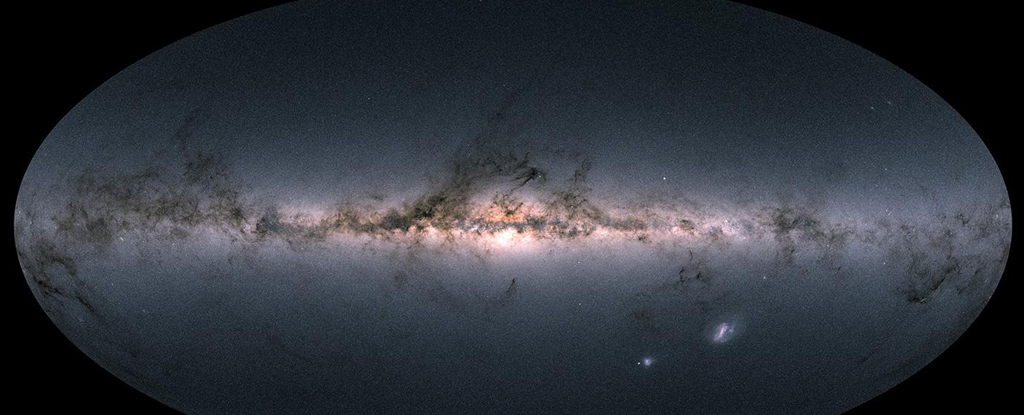

The Milky Way is only as massive as it is because of collisions and mergers with other galaxies.
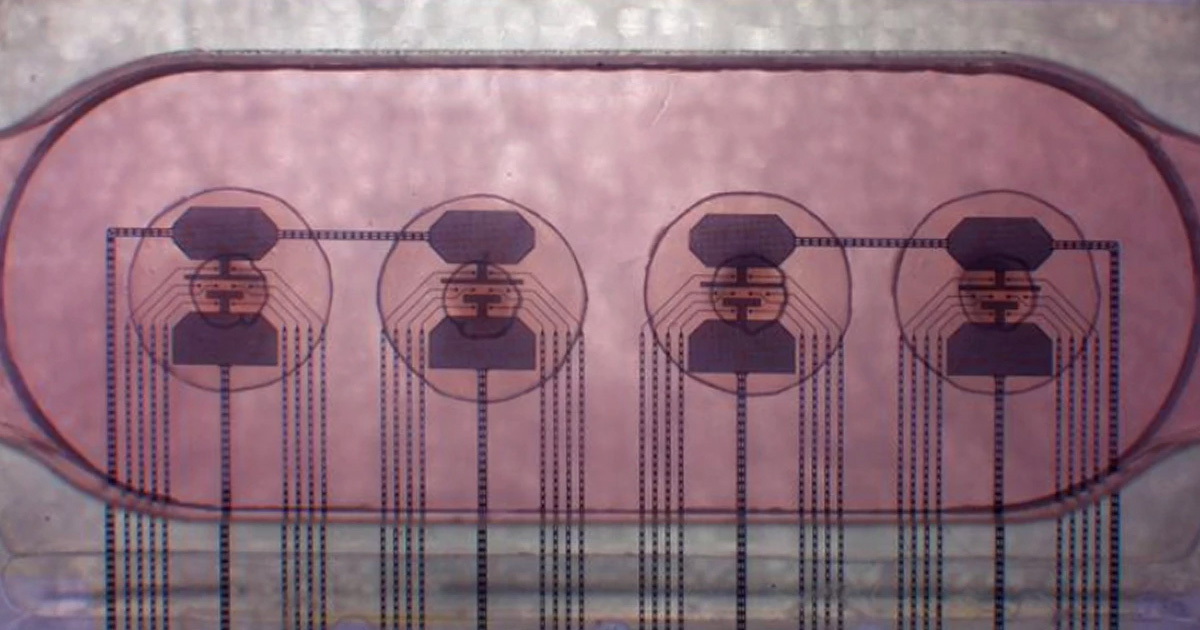
A startup in Switzerland has built a unique computer processor made from 16 tiny brains made from human tissue, basically a living computer.
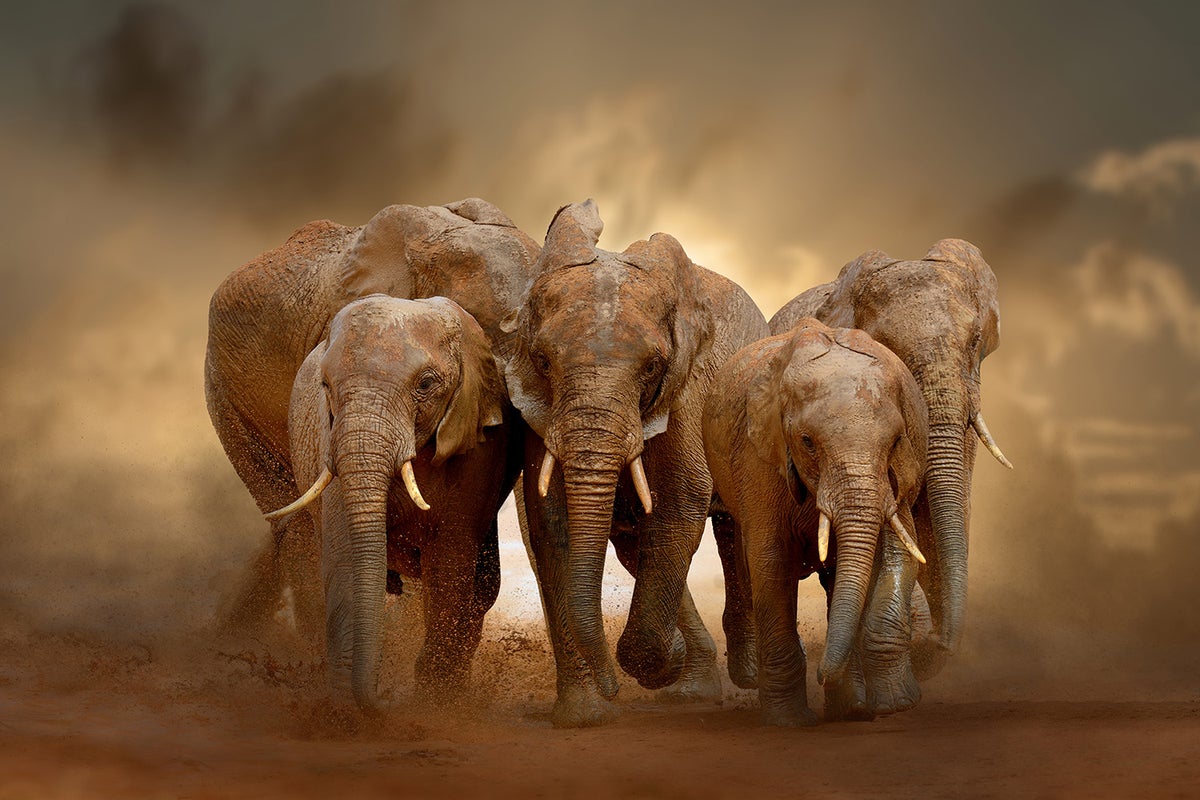

A new research suggests wild African elephants may pick their own names and use them to call and greet one another on the savanna.
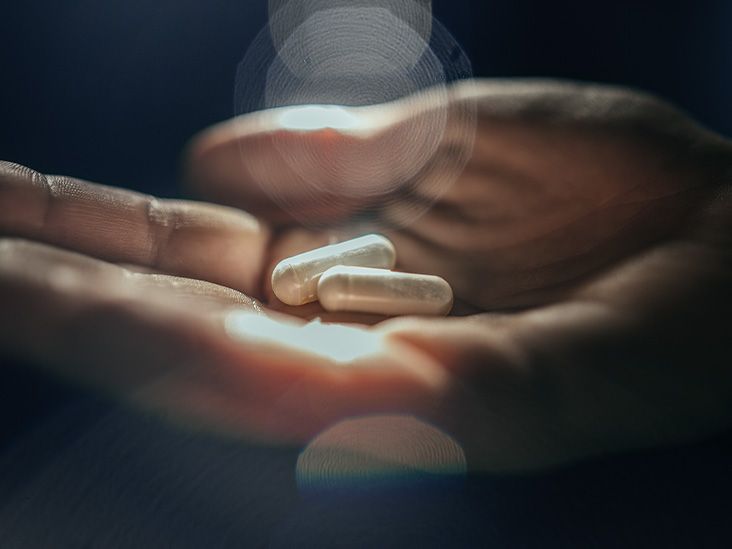

A recent study shows promise for a new antibiotic that effectively fights several bacteria while sparing the helpful bacteria that occur naturally in the gut.
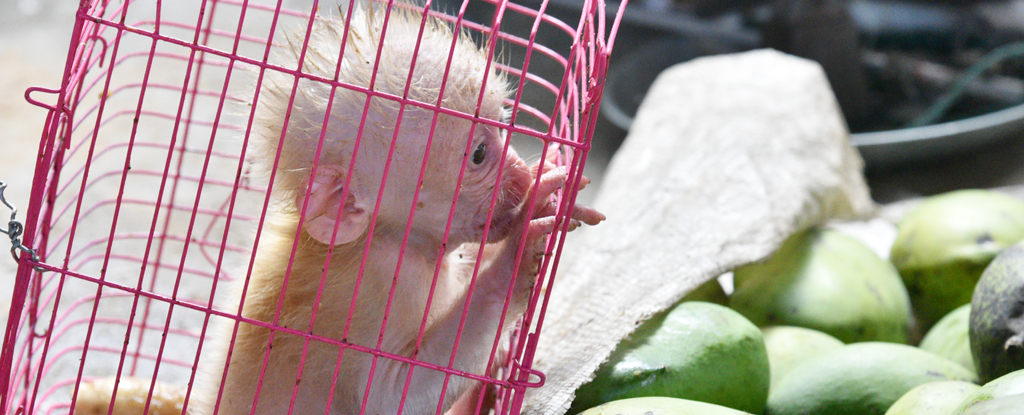

Around 4,000 species of plants and animals are victims of illegal wildlife trade globally, according to the latest World Wildlife Crime Report.
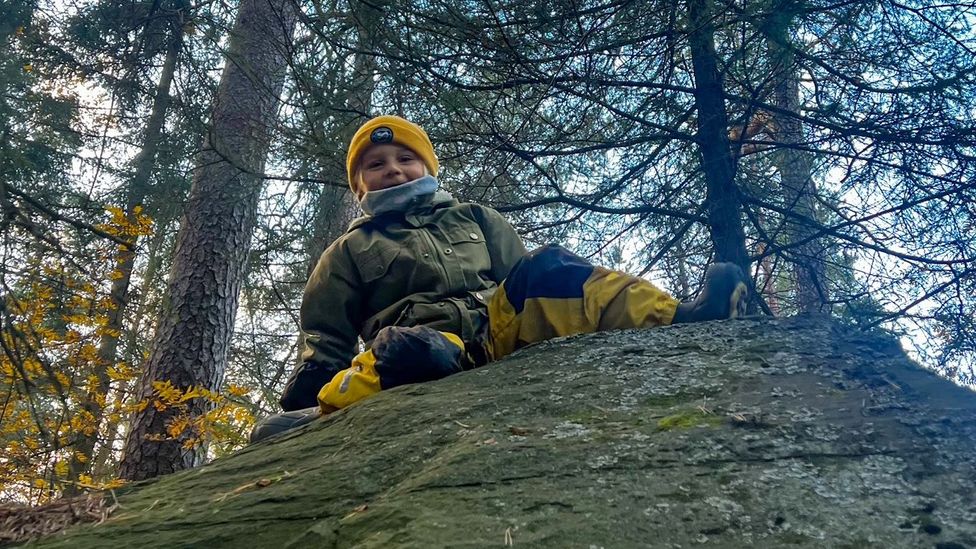

Scandinavian-style forest schools and nurseries are spreading all around the world. Outdoor learning is increasing seen as an important way of connecting children with nature.

The consumption of ultra-processed foods (UPFs) may be associated with insomnia experienced by an estimated one third of adults, a report has revealed.
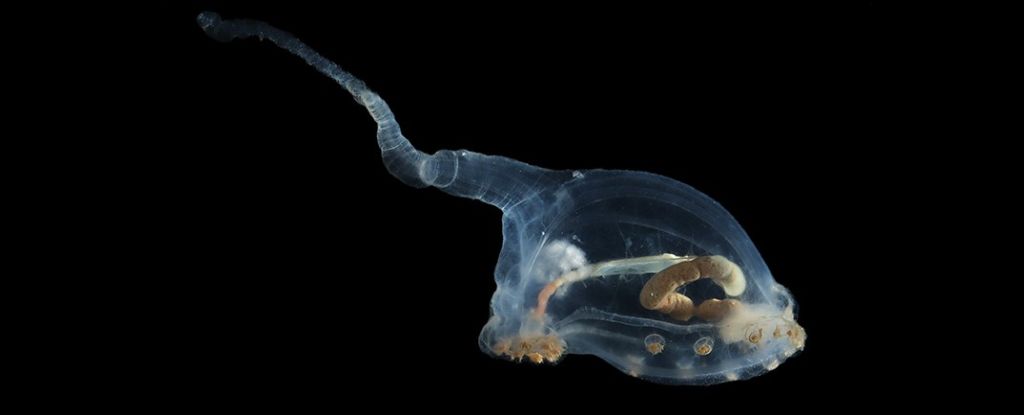

A collection of new species discovered lurking on the seafloor exemplifies exactly how alien this strange world is.
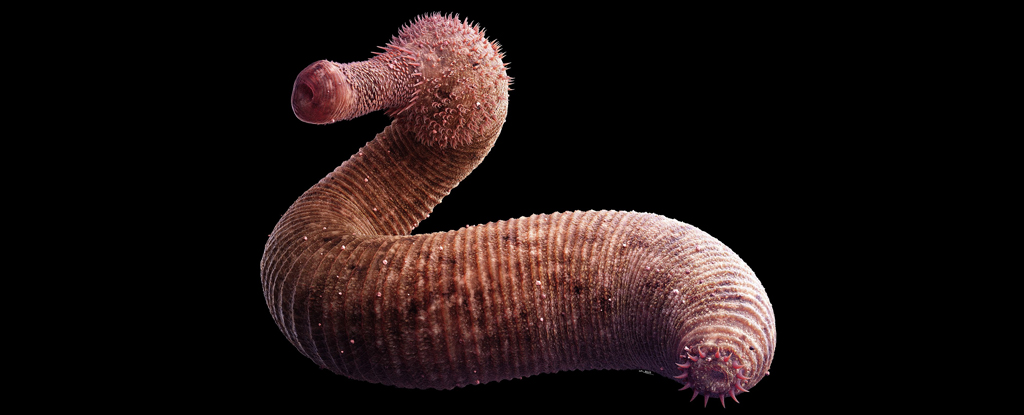
Prehistoric marine worms may have made an outsized contribution to the Great Ordovician Biodiversification Event.

A neutron star labeled ASKAP J1935+2148 defies rules for neutron stars, emitting radio signals on a comparatively leisurely interval of 53.8 minutes.

The creation of any heavier elements would consume energy instead of releasing it. In order to explain the presence of these heavier elements today, it's necessary to find phenomena that can produce them.
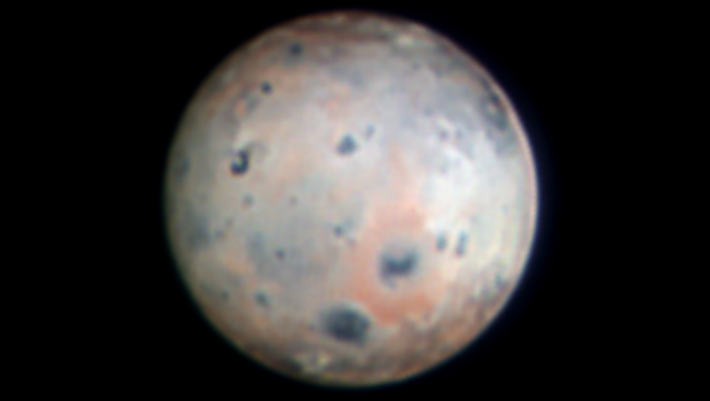

Using the SHARK-VIS instrument on the Large Binocular Telescope on Mount Graham in Arizona, the United States, astronomers have captured the highest resolution optical images of Io ever obtained from a ground-based telescope.
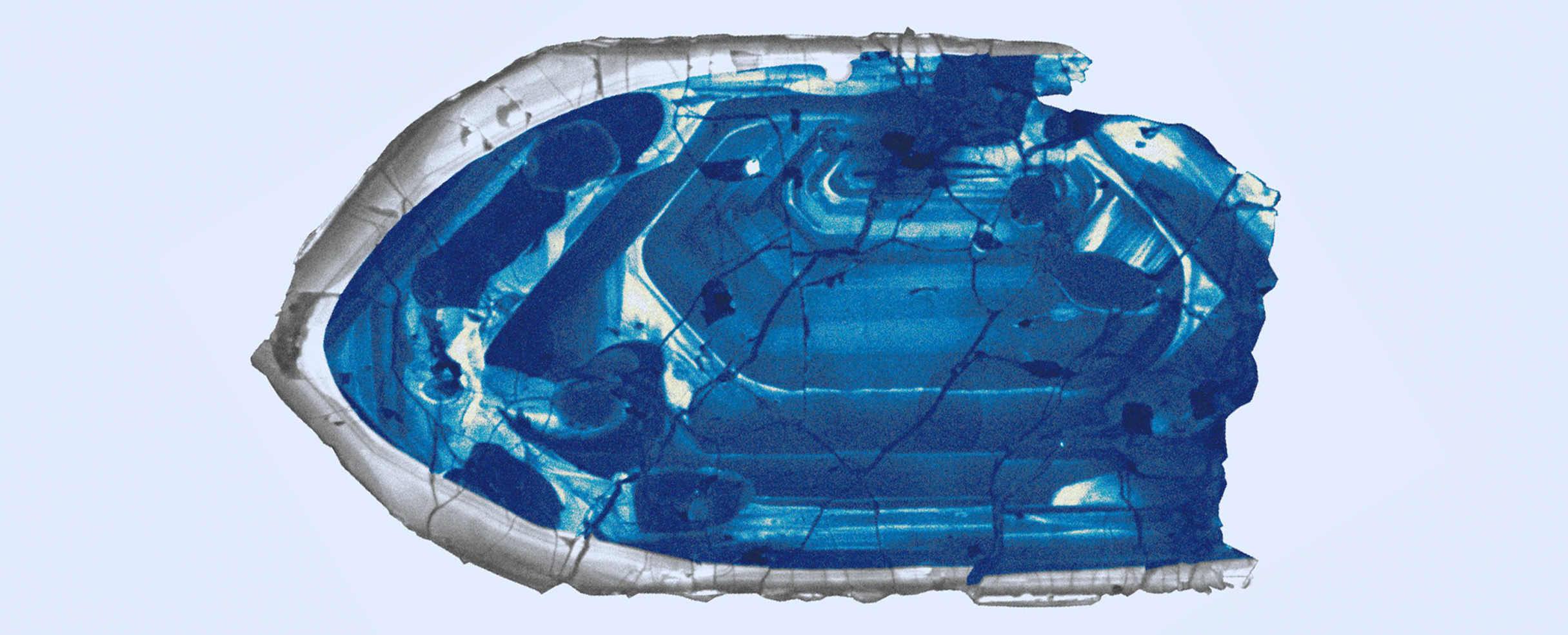
New research finds Earth's surface was first sprinkled with fresh water some 4 billion years ago, a whole 500 million years earlier than previously thought.