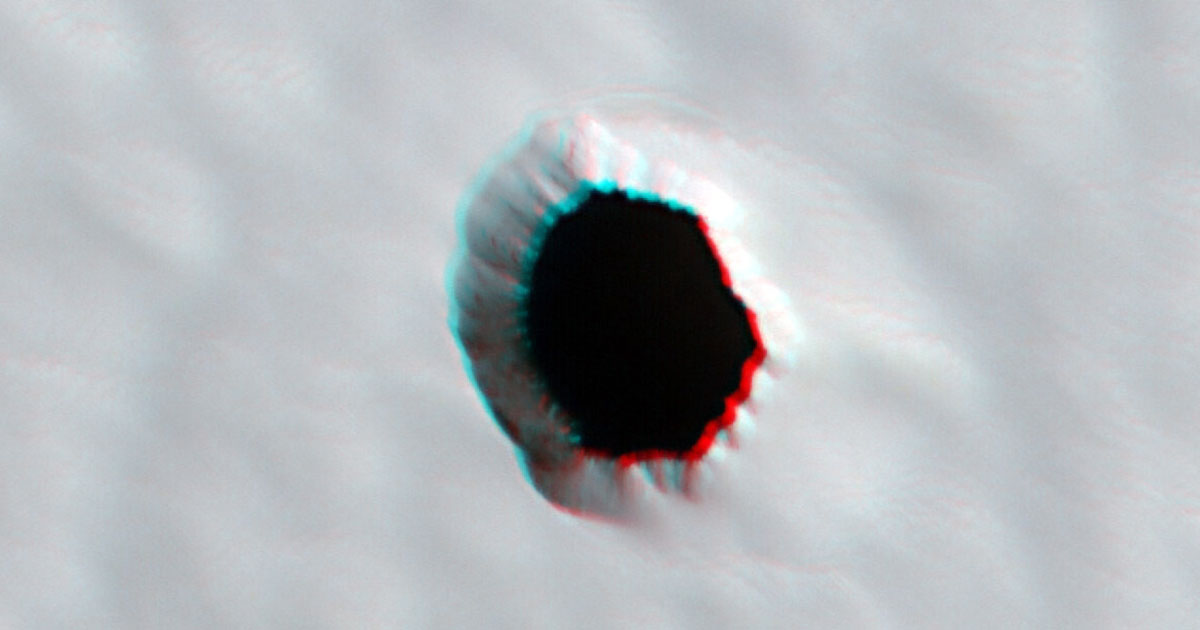

NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) has discovered another intriguing formation on the planet's barren surface. Despite their best efforts, scientists can only guess as to how exactly holes like this one were formed.
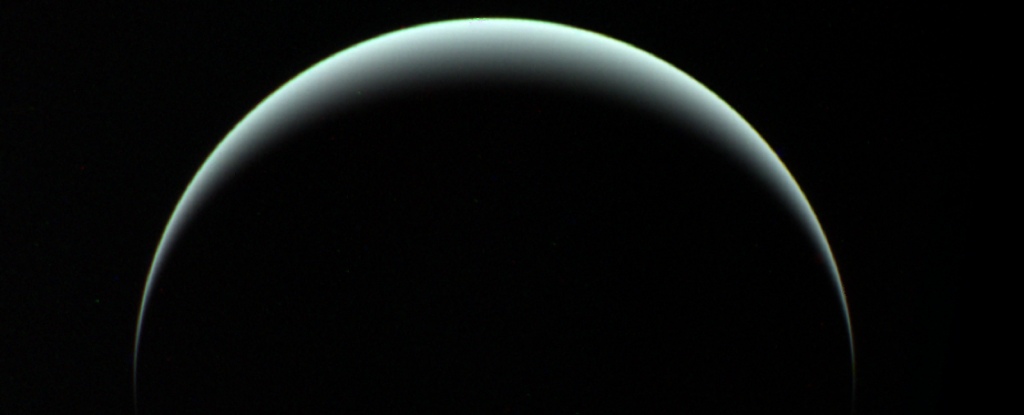

One of the most peculiar things about Uranus and Neptune is their magnetic fields.

One of the most peculiar things about Uranus and Neptune is their magnetic fields.
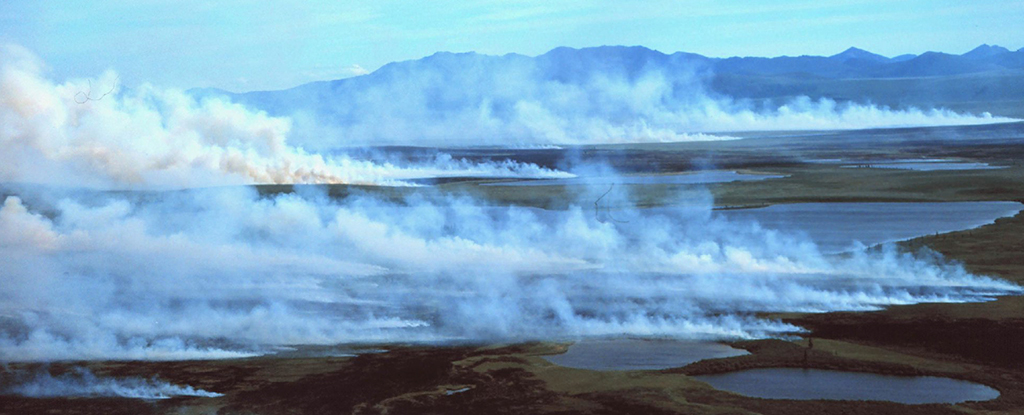

These fires puzzle scientists because they appear in early May, way ahead of the usual fire season in the far north, and can reignite for a number of years.
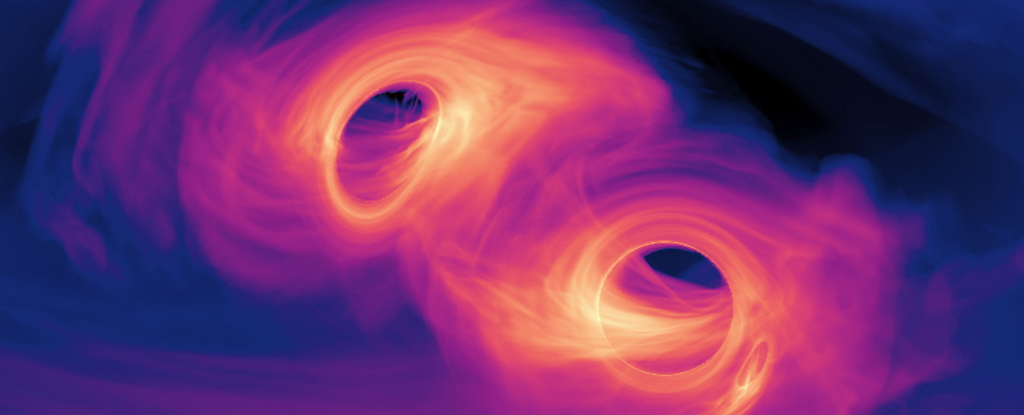

The researchers say that these black holes mergers are a window into Hawking Radiation. When black holes merge, they may create so-called "morsel" black holes the size of asteroids that are ejected into space.
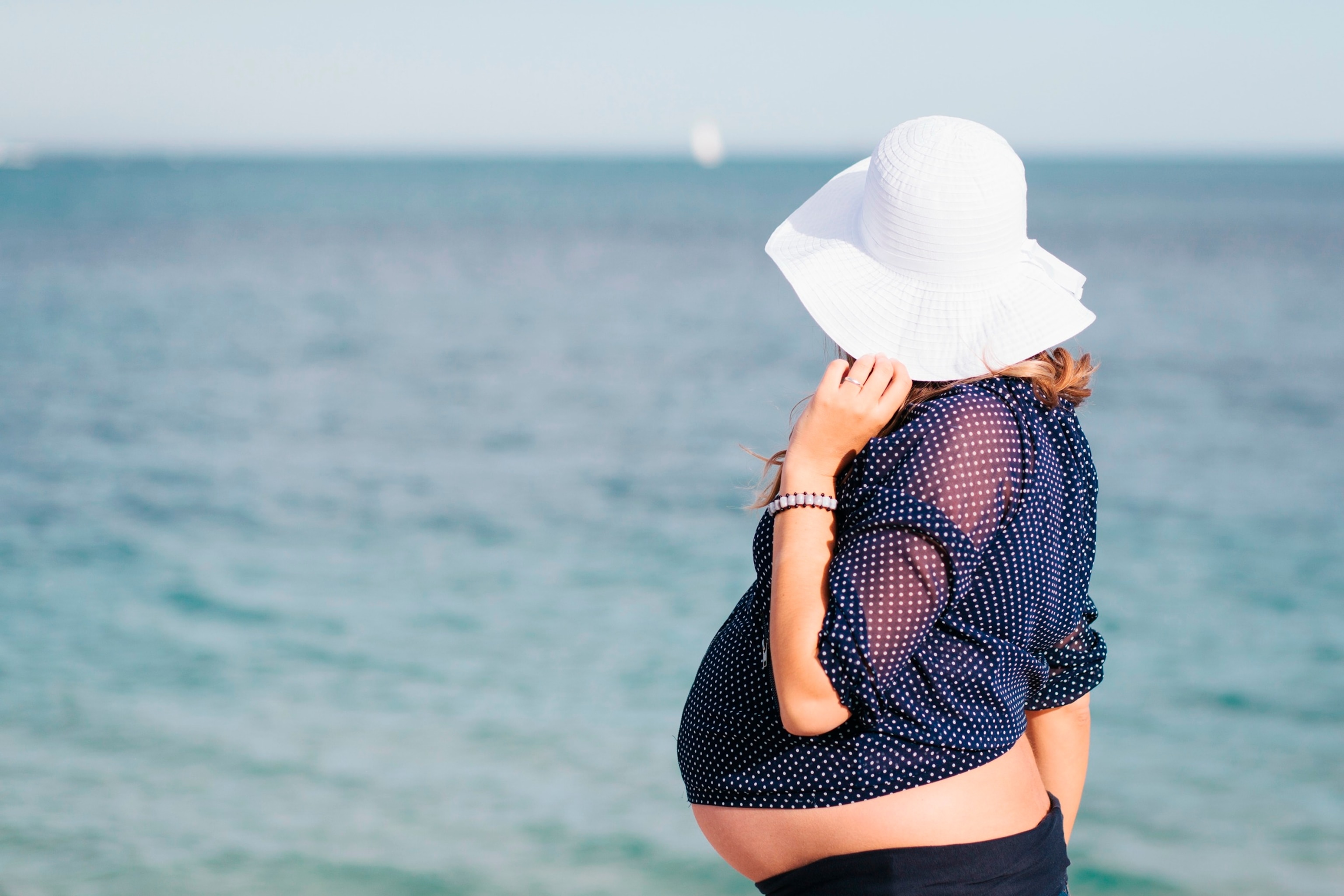

As the world braces for another summer of extreme heat, following the record-setting 2023 season, a recent study has acutely linked heat waves to the rate of early births among pregnant women.
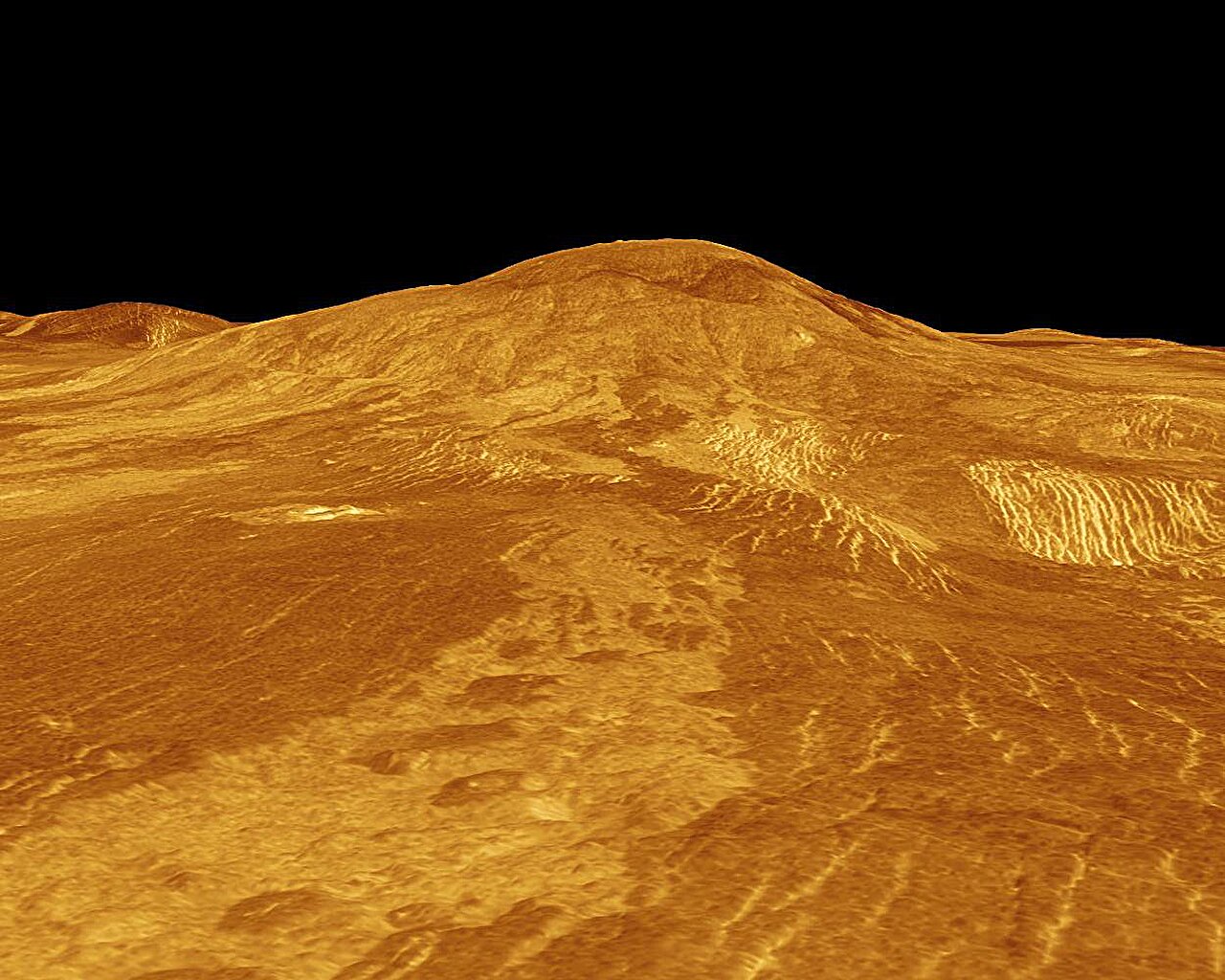
A new analysis of data collected on Venus more than 30 years ago suggests the planet may currently be volcanically active.

It turns out that certain black holes act just like the terrifying sci-fi battle station, spinning around to fire giant beams at various targets in the cosmos.
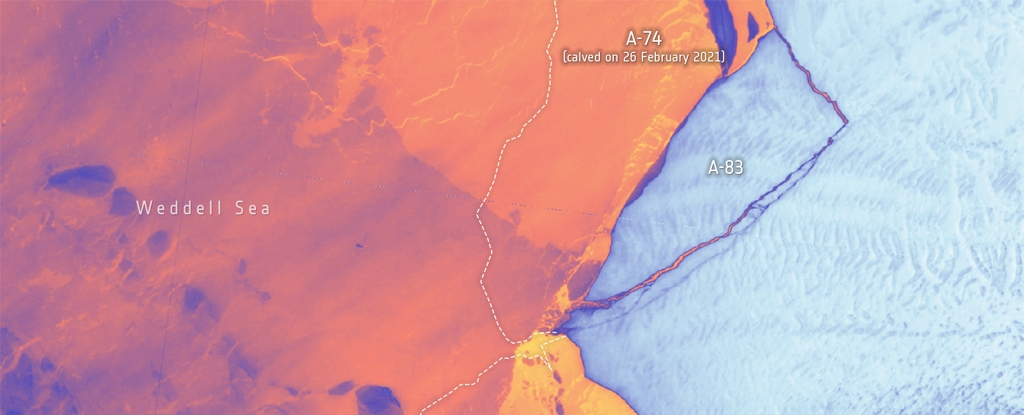
On May 20th, 2024, an iceberg measuring 380 square kilometers broke off the Brunt Ice Shelf in Antarctica. This event (A-83) is this region's third significant iceberg calving in the past four years.
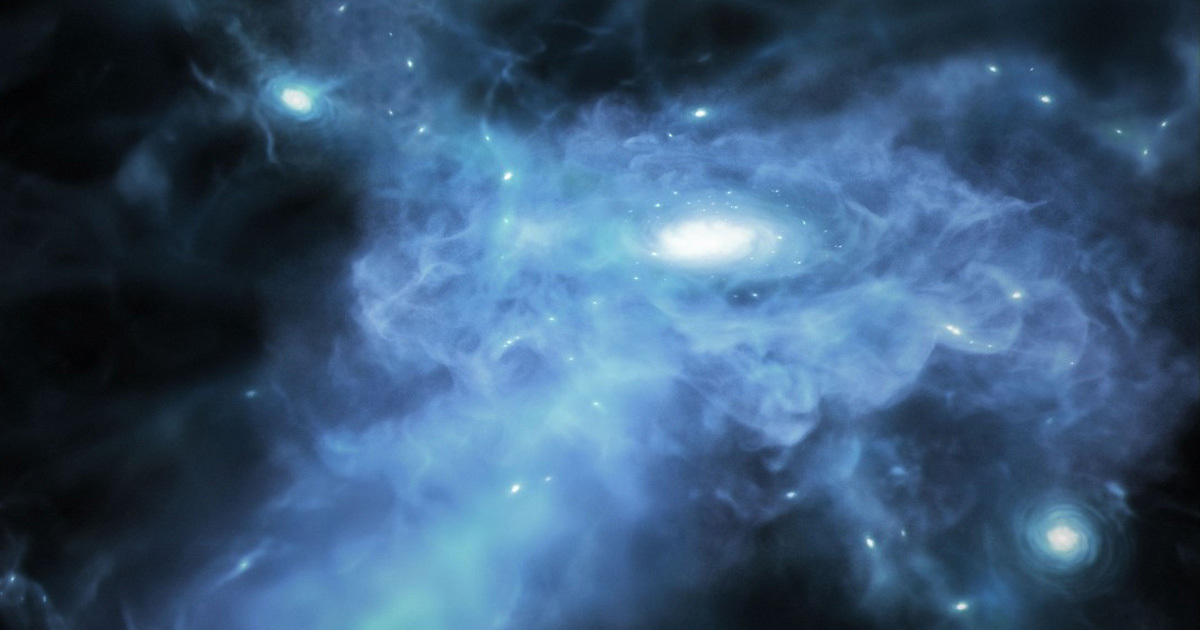

Using the James Webb Space Telescope, researchers observed the birth of some of the youngest galaxies ever witnessed.
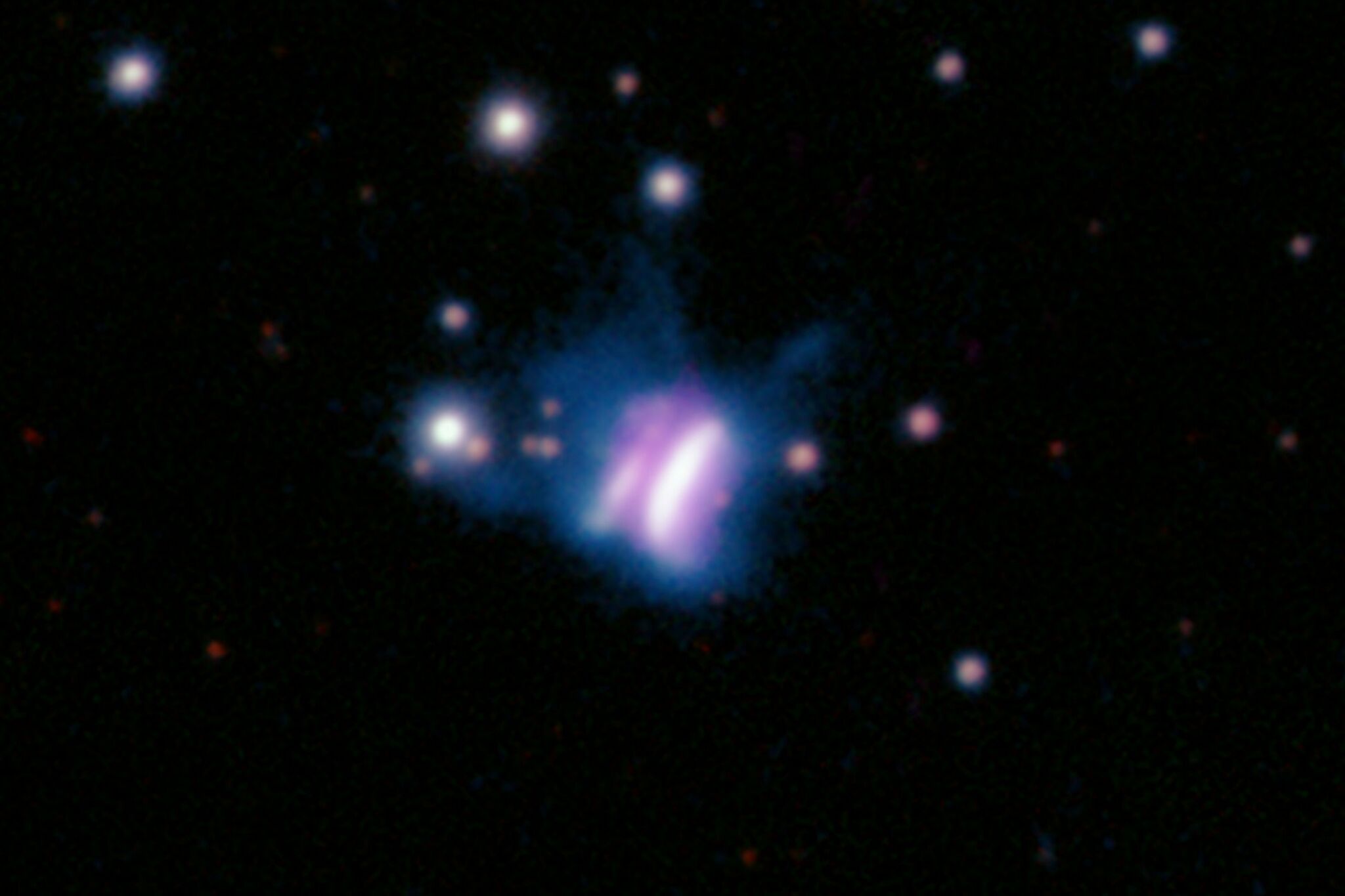

Astronomers discover the biggest planet-forming disk ever and it resembles a butterfly.

The Euclid mission, led by ESA (the European Space Agency) with contributions from NASA, has released five new images that showcase the space telescope’s ability to explore two large-scale cosmic mysteries: dark matter and dark energy.
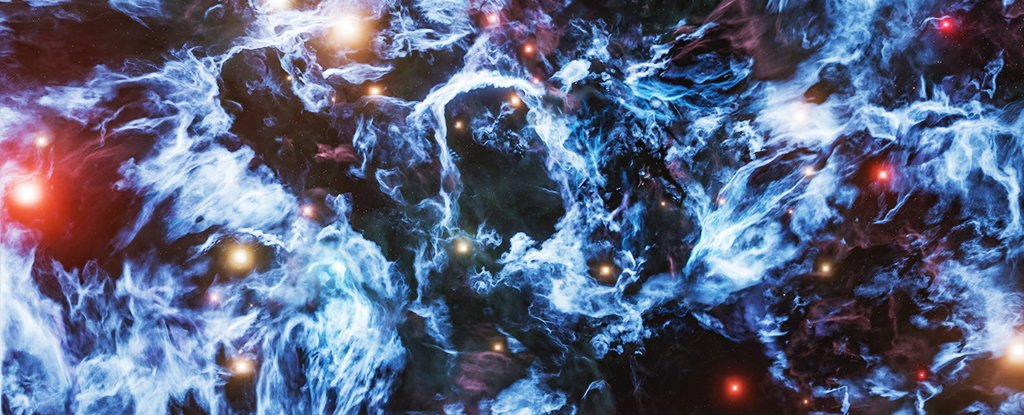

A new study suggests that gravity becomes about 1% weaker at very large scales. If gravity behaved according to Einstein's theory, then this 1% difference shouldn't exist.

Six of the planets of the Solar System are about to line up for a rare sight in Earth's sky.
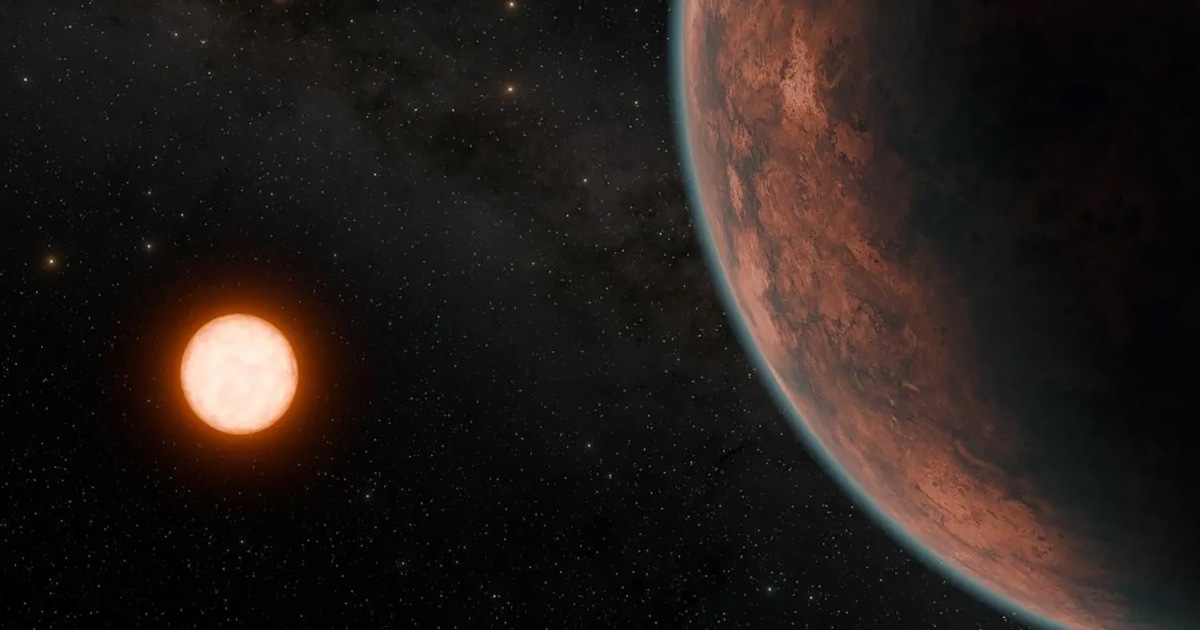

Dubbed Gliese 12 b, the planet takes 12.8 days to orbit a star that is 27% of the sun's size. The planet is about the size of Venus, so slightly smaller than Earth, and may be temperate enough to support life, the researchers said.