
The radio telescope array ALMA has pin-pointed the exact cosmic age of a distant JWST-identified galaxy, GHZ2/GLASS-z12, at 367 million years after the Big Bang.

Researchers from Montreal and India have captured a radio signal from the most distant galaxy so far at a specific wavelength known as the 21 cm line, this is the first time this type of radio signal has been detected at such a large distance.

James Webb Space Telescope has captured light emitted by the galaxies more than 13.4 billion years ago, which means the galaxies date back to less than 400 million years after the Big Bang, when the universe was only 2 % of its current age.

A powerful European Ariane 5 rocket boosted NASA’s $10 billion James Webb Space Telescope into space on Christmas Day, kicking off a great attempt to capture light from the first galaxies to form in the aftermath of the Big Bang.

Astronomers have spotted two close pairs of quasars in the process of merging as their host galaxies crash together in a slow-motion collision 10 billion years ago. Quasars make a profound impact on galaxy formation.

Astronomers have discovered the most distant source of radio emission known to date - the quasar, nicknamed P172+18. It is so distant that light from it has travelled for about 13 billion years to reach us.

Astronomers are studying black holes that could have formed in the early universe, before stars and galaxies were born. Such primordial black holes (PBHs) could account for all or part of dark matter.

Astronomers have found six galaxies lying around a supermassive black hole when the Universe was less than a billion years old. This is the first time such a close grouping has been seen so soon after the Big Bang.
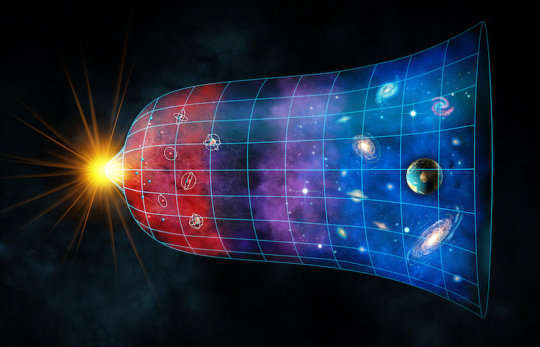
Recently scientists suggested that have suggested the universe may be hundreds of millions of years younger. However a new observations suggest the universe is still about 13.8 billion years old.

The universe is full of billions of galaxies. Why do we see so much structure in the universe today? A 10-year survey of tens of thousands of galaxies has provided a new approach to answering this fundamental mystery.

Astronomers have detected large amounts of oxygen in the atmosphere of one of the oldest and most elementally depleted stars known. This finding provides an important clue on how oxygen was produced in the first generations of stars.

Data obtained by VLT showed evidence of massive stars bursts billions of years ago in the galaxy’s center. The more recent burst was so intense that resulted in 100,000 supernova explosions. These findings are inconsistent with our notions that stars formed continuously in our galaxy.

Astronomers have spotted an unusually distant star-forming galaxy, the light of which took a whopping 13 billion years to reach Earth. Perhaps most incredibly, however, the galaxy was observed directly, without gravitational lensing.

An international team of astronomers led by the University of Tokyo used ALMA to view 39 previously-undiscovered ancient galaxies, a find that could have major implications for astronomy and cosmology.

Within 100,000 years of the Big Bang, the very first molecule emerged, an improbable marriage of helium and hydrogen known as a helium hydride ion, or HeH+. It was the beginning of chemistry.